Research by: Israel Gubi
During the past week, Check Point Research spotted a new version of Azorult in the wild being delivered through the RIG exploit kit, as well as other sources. Azorult is a long known information stealer and malware downloader, with this particular version being advertised in an underground forum since October 4. The version number given to it by its authors is 3.3.
There are quite a few changes in this newly witnessed variant, the most prominent ones being a new encryption method of the embedded C&C domain string, a new connection method to the C&C and improvement of the Crypto currency wallets stealer and loader.
The timing of this update to the malware is not surprising, mainly in light of major leaks for previous versions 3.1 and 3.2, in which panel source code and binary builders were released for the public to use for free. Check Point shared those leaks to the research community for further investigation last month. Moreover, we have witnessed and written about another project related to Azorult, dubbed ‘Gazorp’ – a dark web binary builder that allows anyone to craft the malware’s binaries for free. Having this in minds, it is plausible that the Azorult’s author would like to introduce new features to the malware and make it worthy as a product in the underground market.
The Forum Advertisement
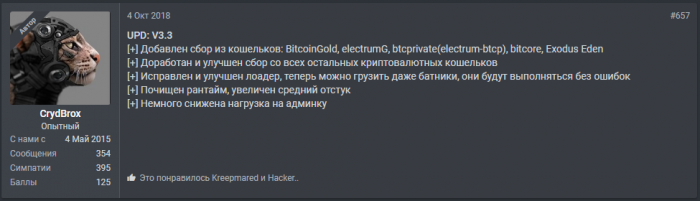
On October 4, the following update to Azorult was advertised on the exploit.in underground forum by the user CrydBrox. The updated version number 3.3 is shown below.
Figure 1: Advertisement of Azorult v3.3
The above states the following improvements and features:
[+] Added support for stealing the following wallet credentials: BitcoinGold, electrumG, btcprivate (electrum-btcp), bitcore, Exodus Eden
[+] Cryptocurrency wallet’s stealer component has been improved.
[+] The loader component was fixed and improved, allowing bat files to be loaded and executed with no errors
[+] Lowered AV detection rate, increased successful installation rate
[+] Slight improvement in admin panel’s performance
Comparison to previous versions
- In version 3.2, the C&C domain name was xored with a hardcoded key and then encoded with base64. The current version 3.3 shows a new encryption method to obfuscate the domain name. The script for decryption of the domain’s string can be found in the Appendix below.
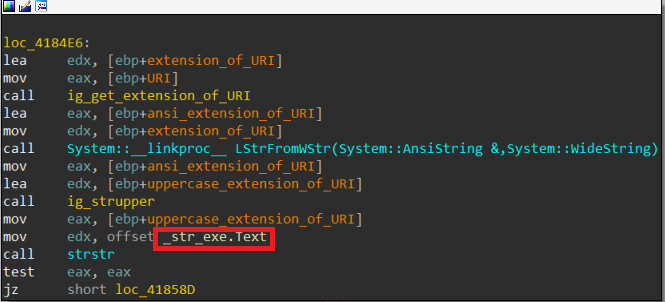
- Every version of Azorult has a unique xor key for its connection method to the C&C. In version 3.3 the connection key is: [0x3, 0x55, 0xae]. Moreover, every version connection message contains a prefix (‘getcfg=’ in version 3.1 and ‘G’ in version 3.2) prepended to the id hash before xoring with the connection key. The prefix in version 3.3 is the connection key, which makes the connection message sent to C&C starts with 3 zero bytes.
Figure 2: adding connection key as prefix.
- Azorult’s C&C server response is divided into 3 parts separated by tags:
<c></c> – the configuration part, encoded with base64
<n></n> – DLLs that Azorult copies to a new directory it creates under the %TEMP% folder. The name of the new directory is unique for every version of Azorult (‘1M0’ in version 3.1 and ‘2fda’ in version 3.2). In the new version, the name of the directory is generated based on the id hash of the victim’s computer. Therefore, the name of the directory will be different for every victim.
The algorithm for generating the directory name is as follows:
Id_hash=hash_func(guid)-hash_func(product_name)-hash_func(user_name)- hash_func(computer_name)-hash_func(guid+product_name+user_name+computer_name)
Directory_name = hash_func(hash_func(Id_hash))
The particular implementation of the hash_func method is outlined in a script, which appears in the Appendix below.
<d></d> – names of application paths that Azorult harvests data from. In version 3.3,
The following application names are added:
%appdata%\ElectrumG\wallets\
\ElectrumG
%appdata%\Electrum-btcp\wallets\
\Electrum-btcp
BitcoinGold\BitcoinGold-Qt
BitCore\BitCore-Qt
BitcoinABC\BitcoinABC-Qt
%APPDATA%\Exodus Eden\
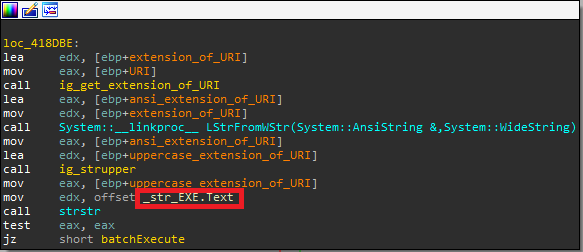
The authors of Azorult fixed a bug in the loader functionality that didn’t allow the malware to load bat files and execute them successfully. The bug was caused by wrongfully comparing the extension of the loaded file, causing the launch of all files with CreateProcessW API as executables instead of ShellExecuteExW. In the new version, the authors fixed the comparison method to avoid this bug.
Figure 3: loader extension comparison in versions 3.2 and 3.3. The former introduces a bug.
Appendix
- C&C domain name decryption Python code:
def decrypt_domain_method_v3_3(encrypted_domain):
decrypted_domain_array = []
key_buffer = [0x1e, 0x15, 0x34, 0x49, 0x5e, 0x37, 0x24, 0x2f, 0x58, 0x27, 0x6e, 0xd3, 0xd4, 0x71, 0xd6, 0x73, 0xd8]
index = 0
sum = 0
while index < len(encrypted_domain):
cur_byte = encrypted_domain[index]
if cur_byte == key_buffer[0]:
sum += 0x64
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[1]:
sum += 0x5a
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[2]:
sum += 0x50
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[3]:
sum += 0x46
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[4]:
sum += 0x3c
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[5]:
sum += 0x32
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[6]:
sum += 0x28
elif cur_byte == key_buffe[7]:
sum += 0x1e
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[8]:
sum += 0x14
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[9]:
sum += 0x0a
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[10]:
sum += 0x8
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[11]:
sum += 0x6
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[12]:
sum += 0x5
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[13]:
sum += 0x4
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[14]:
sum += 0x2
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[15]:
sum += 0x1
elif cur_byte == key_buffer[16]:
decrypted_domain_array.append(chr(sum))
sum = 0
elif cur_byte == 0:
break
index += 1
decrypted_domain = ”.join(decrypted_domain_array)
return decrypted_domain
- hash_func method for calculating the generated directory name.
def hash_func(value):
xor_key = 0x6521458a
hash_output = 0
for index in range(len(value)):
cur_byte = ord(value[index])
xor_value = cur_byte ^ xor_key
hash_output = (hash_output + xor_value) % (2**32)
right_value = (hash_output << 0xd) % (2**32)
left_value = (hash_output >> 0x13) % (2**32)
diff_value = right_value | left_value % (2**32)
hash_output = (hash_output – diff_value) % (2**32)
hash_string = hex(hash_output)[2:-1]
if len(hash_string) < 8:
diff = 8 – len(hash_string)
output_string = (‘0’ * diff) + hash_string
else:
output_string = hash_string
output_string = output_string.upper()
return output_string
IOCs
Md5:
11147fd9ac12eec66d35b4d483aae71f
d893d8347ecad1a3d85064d2f5bded4f
a8d3e403995132f9af33e4557be301a0
C&C:
http://infolocalip.com/index.php
http://tohertgopening.com/index.php
TE signature: InfoStealer.Win.AZORult.C